Page 357 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 357
Core network aspects 1
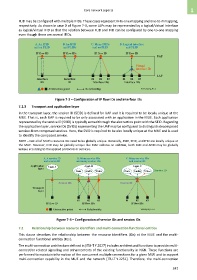
FLID may be configured with multiple IFIDs. These cases represent N-to-one mapping and one-to-N mapping,
respectively. As shown in case D of Figure 7-3, some LAPs may be represented by a logical/virtual interface
as logical/virtual IFID so that the relation between FLID and IFID can be configured by one-to-one mapping
even though there are several IFIDs.
A. An IFID B. An IFID C. Many IFIDs D. Logical interface
and an FLID and FLIDs and an FLID and FLID
IP flow ID IP flow IDs IP flow ID IP flow ID
UAP
Virtual
interface ID
LAP
Interface Interface #1 #2 #3 #1 #2 #3
ID ID Interface IDs Interface IDs
Abstraction point Relationship Y.2252(12)_F7-3
Figure 7-3 – Configuration of IP flow IDs and interface IDs
7.1.3 Transport and application layer
In the transport layer, the session ID (SEID) is defined for UAP and it is required to be locally unique at the
MUE. That is, each UAP is required to be only associated with an application in the MUE. Each application
represented by the service ID (SVID) is typically served through the abstraction point with the SEID. Regarding
the application layer, service IDs (SVIDs) representing the UAP may be configured to distinguish decomposed
services from composed services. Here, the SVID is required to be also locally unique at the MUE and is used
to identify the composed service.
NOTE – Not all of MUE's resource IDs need to be globally unique. Generally, SVID, SEID, and IFID are locally unique at
the MUE. However, IFID may be globally unique like MAC address. In addition, both FLID and ANID may be globally
unique according to the applied protocols or services.
A. A service ID B. Many service IDs C. Many service IDs
and session ID and many session IDs and session ID
Application Appl. A Appl. B Appl. C
layer
Data Audio Video Data Audio Video Service ID
Session IDs Session ID
Transport
layer
#1 #2 #3 #1 #2 #3
IP flow ID IP flow IDs IP flow IDs
Abstraction point Relationship Y.2252(12)_F7-4
Figure 7-4 – Configuration of service IDs and session IDs
7.2 Relationship between resource identifiers and multi-connection functional entities
This clause describes the relationship between the resource identifiers (IDs) at the MUE and the multi-
connection functional entities (FEs).
The multi-connection architecture defined in [ITU-T Y.2027] includes architectural functions to provide multi-
connection related signalling and enhancements of the existing functionality in NGN. These functions are
performed to maintain information of the concurrent multiple connections for a given MUE and to support
multi-connection capability in the MUE and the network [ITU-T Y.2251]. Therefore, the multi-connection
347