Page 353 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 353
Core network aspects 1
Applications
Multi-connection
control function
Multi-connection
Multi-connection application
Application layer support function (MAS-F) policy control FE
Multi-connection
Transport layer Service control function(SCF) user profile FE
Multi-connection
coordination FE
Multi-connection media function Multi-connection
(MMF) registration FE
Access control FE Access control FE
Network layer
(AC-FE) (AC-FE) MUE
Multi-connection
PHY/MAC layer Access network Access network terminal control
function
Y.2252(12)_F6-1
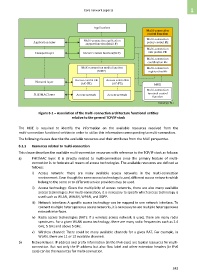
Figure 6-1 – Association of the multi-connection architecture functional entities
relative to the general TCP/IP stack
The MUE is required to identify the information on the available resources received from the
multi-connection functional entities in order to utilize this information corresponding to multi-connection.
The following clauses describe the available resources and their attributes from the MUE perspective.
6.1.1 Resources related to multi-connection
This clause describes the available multi-connection resources with reference to the TCP/IP stack as follows:
a) PHY/MAC layer: It is directly related to multi-connection since the primary feature of multi-
connection is to federate all means of access technologies. The available resources are defined as
follows:
i) Access network: There are many available access networks in the multi-connection
environment. Even though the same access technology is used, different access networks which
belong to the same or to different service providers may be used.
ii) Access technology: Given the multiplicity of access networks, there are also many available
access technologies. For multi-connection, it is necessary to specify which access technology is
used such as WLAN, WWAN, WPAN, and 3GPP.
iii) Network interface: A specific access technology can be mapped to one network interface. To
connect multiple heterogeneous access networks, it is necessary to use multiple heterogeneous
network interfaces.
iv) Radio access technologies (RAT): If a wireless access network is used, there are many radio
spectrums. For a given WLAN access technology, there are many radio frequencies such as 2.4
GHz, 5 GHz and above 5 GHz.
v) Wireless channel: There could be many available channels for a given RAT. For example, in
WLAN, there are 11 or 13 available channels.
b) Network layer: IP address and prefix information (in the IPv6 case) are typical resources for multi-
connection. But not only the IP address but also flow label and other extension headers (in IPv6
case) can be the resources for multi-connection.
343