Page 1050 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 1050
2 Transport aspects
where:
εr = the relative dielectric constant of the dielectric between the outer shield and the
core
Table X.21 – Typical coaxial cable characteristic [b-Large]
Cable Type d (mm) D (mm) Z0 (Ohm) RDC(Ohm/km) C(pF/m) Vp
RG-6 1.024 4.7 75 18.04 53 0.83
RG-59 0.58 3.7 75 33.292 67 0.68
RG-11 1.63 7.25 75 5.6 66 0.84
The relative propagation velocity is the ratio between velocity in cable and the free-space velocity which is
8
near the speed of light at 3 x 10 m/sec or 984 ft/µs.
1
=
√ ε
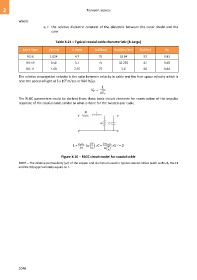
The RLGC parameters could be derived from these basic circuit elements for construction of the impulse
response of the coaxial cable similar to what is done for the twisted-pair cable.
μ 2πε
L = ln ( ) ; C = ; G ~ = 0
2 ln( )
Figure X.10 – RLGC circuit model for coaxial cable
NOTE – The relative permeability (µr) of the copper and aluminium used in typical coaxial cables (such as RG-6, RG-11
and RG-59) approximately equals to 1.
1040