Page 794 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 794
6.2.4 Quality of life
This clause lists the core indicators defined for Quality of Life.
There are 7 indicators in this dimension, covering e‐learning, electronic health records, electronic
medical records, sharing medical information, telemedicine, anti‐disaster and other safety
measures.
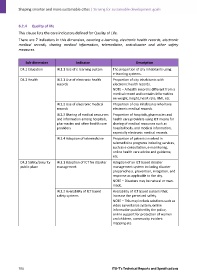
Sub‐dimension Indicator Description
D4.1 Education I4.1.1 Use of e‐learning system The proportion of city inhabitants using
e‐learning systems.
D4.2 Health I4.2.1 Use of electronic health Proportion of city inhabitants with
records electronic health records.
NOTE – A health record is different from a
medical record and contains information
on weight, height, heart rate, BMI, etc.
I4.2.2 Use of electronic medical Proportion of city inhabitants who have
records electronic medical records.
I4.2.3 Sharing of medical resources Proportion of hospitals, pharmacies and
and information among hospitals, health care providers using ICT means for
pharmacies and other health care sharing of medical resources such as
providers hospital beds, and medical information,
especially electronic medical records.
I4.2.4 Adoption of telemedicine Proportion of patients involved in
telemedicine programs including services,
such as e‐consultation, e‐monitoring,
online health care advice and guidance,
etc.
D4.3 Safety/security I4.3.1 Adoption of ICT for disaster Adoption of an ICT based disaster
public place management management system including disaster
preparedness, prevention, mitigation, and
response as applicable to the city.
NOTE – Disasters may be natural or man‐
made.
I4.3.2 Availability of ICT based Availability of ICT based systems that
safety systems increase the perceived safety.
NOTE – This may include solutions such as
video surveillance system, online
information published by the police,
online support for protection of women
and children, community incident
mapping etc.
784 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications