Page 381 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 381
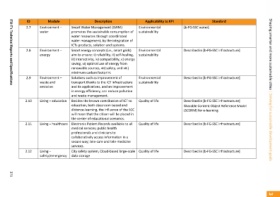
Standard Described in [b‐FG‐SSC infrastructure] Described in [b‐FG‐SSC infrastructure] Described in [b‐FG‐SSC infrastructure] Sharable Content Object Reference Model Described in [b‐FG‐SSC infrastructure] Described in [b‐FG‐SSC infrastructure]
[b‐FG‐SSC water] (SCORM) for e‐learning
Applicability to KPI Environmental sustainability Environmental sustainability Environmental sustainability Quality of life Quality of life Quality of life
Smart Water Management (SWM) water resources through coordinated ICTs products, solution and systems. saving, vi) optimal use of energy from minimum carbon footprint Solutions such as improvement of and waste management. education, both classroom‐based and the center of educational scenarios. medical services; public health professionals and clinicians to services. data storage
Description promotes the sustainable consumption of water management, by the integration of Smart energy concepts (i.e., smart grids) aim to ensure: i) reliability, ii) self‐healing, iii) interactivity, iv) compatibility, v) energy renewable sources, vii) safety, and viii) transport thanks to the ICT infrastructure and its applications, and an improvement in energy efficiency, can reduce pollution Besides the known contribution of ICT to dist
Module Environment – water Environment – energy Environment – waste and emission Living – education Living – healthcare Living – safety/emergency
ID 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 371