Page 254 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 254
Mainly, optical cables are used for backbone broadband network. However, wireless broadband
technology complement to the optical cables is also required to meet the telecommunication
demand for more flexibility.
In some cases, it is difficult to lay cables. Such cases include providing services around waterway
crossings and between buildings. In other cases, it is not efficient to lay cables. Such cases include
providing services for use at temporary events and for rapid network recovery in emergency
occasions like big natural disasters.
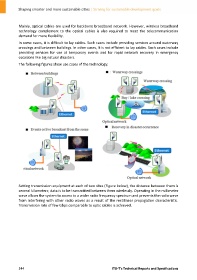
The following figures show use cases of the technology:
Setting transmission equipment at each of two sites (Figure below), the distance between them is
several kilometers; data is to be transmitted between them wirelessly. Operating in the millimeter
wave allows the system to access to a wider radio frequency spectrum and prevents the radio wave
from interfering with other radio waves as a result of the rectilinear propagation characteristic.
Transmission rate of few Gbps comparable to optic cables is achieved.
244 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications