Page 259 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 259
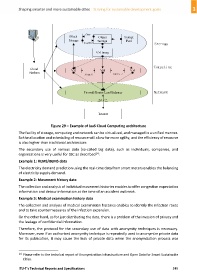
Figure 29 – Example of IaaS Cloud Computing architecture
The facility of storage, computing and network can be virtualized, and managed in a unified manner.
So the allocation and scheduling of resource will allow for more agility, and the efficiency of resource
is also higher than traditional architecture.
The secondary use of various data (so‐called big data), such as individuals, companies, and
14
organizations is very useful for SSC as described :
Example 1: HEMS/BEMS data
The electricity demand prediction using the real‐time data from smart meters enables the balancing
of electricity supply‐demand.
Example 2: Movement history data
The collection and analysis of individual movement histories enables to offer congestion expectation
information and detour information at the time of an accident outbreak.
Example 3: Medical examination history data
The collection and analysis of medical examination histories enables to identify the infection route
and to take countermeasures of the infection expansion.
On the other hand, as for just distributing the data, there is a problem of the invasion of privacy and
the leakage of confidential information.
Therefore, the protocol for the secondary use of data with anonymity techniques is necessary.
Moreover, even if an authorized anonymity technique is repeatedly used to anonymize private data
for its publication, it may cause the leak of private data when the anonymization process was
____________________
14 Please refer to the technical report of Anonymization Infrastructure and Open Data for Smart Sustainable
Cities.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 249