Page 115 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 115
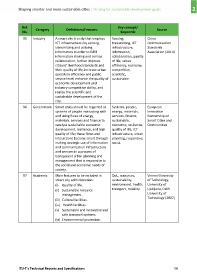
Ref. Category Definitions/Features Key concept/ Source
No. Keywords
95 Industry A smart city is a city that employs Sensing, China
ICT infrastructures by sensing, transmitting, ICT Communication
transmitting and utilizing infrastructure, Standards
information in order to fulfil information, Association (2014)
information sharing and service collaboration, quality
collaboration, further improve of life, urban
citizens' livelihood standards and efficiency, economy,
their quality of life, increase urban competitive,
operation efficiency and public scientific,
service level, enhance the quality of sustainable.
economic development and
industry competitive ability, and
realize the scientific and
sustainable development of the
city.
96 Government Smart cities should be regarded as Systems, people, European
systems of people interacting with energy, materials, Innovation
and using flows of energy, services, finance, Partnership on
materials, services and finance to sustainable, Smart Cities and
catalyse sustainable economic economic, resilience, Communities
development, resilience, and high quality of life, ICT
quality of life; these flows and infrastructure, urban
interactions become smart through planning, responsive,
making strategic use of information social.
and communication infrastructure
and services in a process of
transparent urban planning and
management that is responsive to
the social and economic needs of
society.
97 Academic Main features to be included in QoL, resources, Vienna University
smart city administration: sustainability, of Technology,
(i) Quality of life. environment, health, University of
(ii) Sustainable resource transport, mobility. Ljubljana, Delft
management. University of
Technology (2007)
(iii) Cultural facilities.
(iv) Health facilities.
(v) Sustainable and innovative and
safe transport systems.
(vi) Environmental protection.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 105