Page 110 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 110
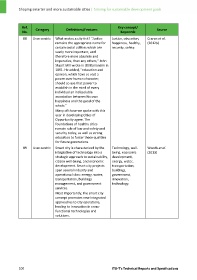
Ref. Category Definitions/Features Key concept/ Source
No. Keywords
88 User centric What makes a city tick? "Justice Justice, education, Craren et al.
remains the appropriate name for happiness, healthy, (2012b)
certain social utilities which are security, safety.
vastly more important, and
therefore more absolute and
imperative, than any others," John
Stuart Mill wrote in Utilitarianism in
1861. He added, "education and
opinion, which have so vast a
power over human character,
should so use that power to
establish in the mind of every
individual an indissoluble
association between his own
happiness and the good of the
whole."
Many of those we spoke with this
year in developing Cities of
Opportunity agree. The
foundations of healthy cities
remain rule of law and safety and
security today, as well as strong
education to foster those qualities
for future generations.
89 User centric Smart city is characterized by the Technology, well‐ Woods et al.
integration of technology into a being, economic (2013)
strategic approach to sustainability, development,
citizen well‐being, and economic energy, water,
development. Smart city projects transportation,
span several industry and buildings,
operational silos: energy, water, government,
transportation, buildings innovation,
management, and government technology.
services.
Most importantly, the smart city
concept promotes new integrated
approaches to city operations,
leading to innovation in cross‐
functional technologies and
solutions.
100 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications