Page 23 - Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities: The Case of Dubai
P. 23
Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities – The Case of Dubai
Under Smart Dubai, there are over 150 “mini-initiatives” and a plan to transform city services
into smart services. These initiatives underpinning Dubai’s smart city objectives are expected to
nurture an open and transparent governance system which can serve its citizens with a seamless
network of urban services designed to improve their overall quality of life (Smart Dubai, 2016).
To achieve this, Smart Dubai aims to encourage collaboration between the public and private
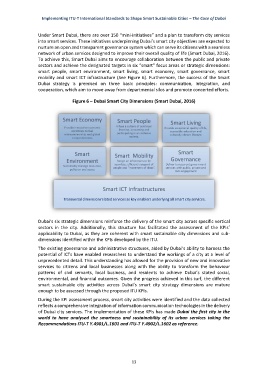
sectors and achieve the designated targets in six “smart” focus areas or strategic dimensions:
smart people, smart environment, smart living, smart economy, smart governance, smart
mobility and smart ICT infrastructure (See Figure 6). Furthermore, the success of the Smart
Dubai strategy is premised on three basic principles: communication, integration, and
cooperation, which aim to move away from departmental silos and promote concerted efforts.
Figure 6 – Dubai Smart City Dimensions (Smart Dubai, 2016)
Dubai’s six strategic dimensions reinforce the delivery of the smart city across specific vertical
sectors in the city. Additionally, this structure has facilitated the assessment of the KPIs’
applicability to Dubai, as they are coherent with smart sustainable city dimensions and sub-
dimensions identified within the KPIs developed by the ITU.
The existing governance and administrative structures, aided by Dubai’s ability to harness the
potential of ICTs have enabled researchers to understand the workings of a city at a level of
unprecedented detail. This understanding has allowed for the provision of new and innovative
services to citizens and local businesses along with the ability to transform the behaviour
patterns of civil servants, local business, and residents to achieve Dubai’s stated social,
environmental, and financial outcomes. Given the progress achieved in this turf, the different
smart sustainable city activities across Dubai’s smart city strategy dimensions are mature
enough to be assessed through the proposed ITU KPIs.
During the KPI assessment process, smart city activities were identified and the data collected
reflects a comprehensive integration of information communication technologies in the delivery
of Dubai city services. The implementation of these KPIs has made Dubai the first city in the
world to have analysed the smartness and sustainability of its urban services taking the
Recommendations ITU-T Y.4901/L.1601 and ITU-T Y.4902/L.1602 as reference.
13