Page 18 - Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities: The Case of Dubai
P. 18
Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities – The Case of Dubai
In effect, the Dubai smart city project forms an integral part of the on-going standardisation
efforts for smart sustainable cities within ITU.
The international standards implemented in Dubai, together with the Recommendation
ITU-T Y.4903/L.1603 “Key performance indicators for smart sustainable cities to assess the
achievement of sustainable development goals”, are expected to set the basis for a KPI
assessment framework for smart sustainable cities on a global level.
The experience derived from Dubai’s implementation of these KPIs will be a key input to the
development of a global set of KPIs for smart sustainable cities to achieve the sustainable
development goals (SDGs). These KPIs are being developed together with 16 UN agencies and
programmes within the United for Smart Sustainable Cities (U4SSC) Initiative which was
established in response to Sustainable Development Goal 11: "Make cities and human
settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable".
Dubai Smart city pilot project will also set the basis for a “Global Smart Sustainable Cities Index”
which is expected to be finalized by July 2017. The work on the Global Smart Sustainable Cities
Index will be supported by the "United for Smart Sustainable Cities" (U4SSC) initiative.
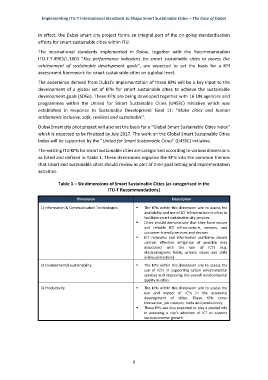
The existing ITU KPIs for smart sustainable cities are categorised according to various dimensions
as listed and defined in Table 1. These dimensions organize the KPIs into the common themes
that smart and sustainable cities should review as part of their goal setting and implementation
activities.
Table 1 – Six dimensions of Smart Sustainable Cities (as categorised in the
ITU-T Recommendations)
Dimension Description
1) Information & Communication Technologies The KPIs within this dimension aim to assess the
availability and use of ICT infrastructure in cities to
facilitate smart sustainable city services.
Cities should demonstrate that they have secure
and reliable ICT infrastructure, services, and
customer-friendly services and devices.
ICT networks and information platforms should
contain effective mitigation of possible risks
associated with the use of ICTs (e.g.
electromagnetic fields, privacy issues and child
online protection).
2) Environmental sustainability The KPIs within this dimension aim to assess the
use of ICTs in supporting urban environmental
services and improving the overall environmental
quality in cities.
3) Productivity The KPIs within this dimension aim to assess the
use and impact of ICTs in the economic
development of cities. These KPIs cover
innovation, job creation, trade and productivity.
These KPIs are also expected to play a pivotal role
in assessing a city’s adoption of ICT to support
socio-economic growth.
8