Page 181 - AI for Good Innovate for Impact
P. 181
AI for Good Innovate for Impact
REQ-06: Expand to Other Diseases: Adapt the platform to study non-respiratory diseases
(e.g., cancer, neurodegenerative disorders), leveraging the modular design of the AI-organoid
system to address diverse medical needs.
REQ-07: Engage Public Awareness: Launch a global campaign to educate the public on 4.1-Healthcare
the benefits of organoid technology and AI in healthcare, fostering trust and encouraging
participation in clinical trials.
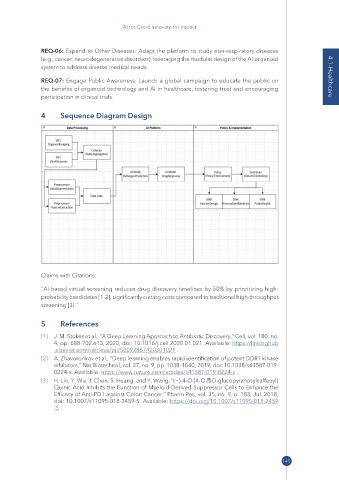
4 Sequence Diagram Design
Claims with Citations:
"AI-based virtual screening reduces drug discovery timelines by 50% by prioritizing high-
probability candidates [1-2], significantly cutting costs compared to traditional high-throughput
screening [3]."
5 References
[1] J. M. Stokes et al., “A Deep Learning Approach to Antibiotic Discovery,” Cell, vol. 180, no.
4, pp. 688-702.e13, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.01.021. Available: https:// linkinghub
.elsevier .com/ retrieve/ pii/ S0092867420301021 .
[2] A. Zhavoronkov et al., “Deep learning enables rapid identification of potent DDR1 kinase
inhibitors,” Nat Biotechnol, vol. 37, no. 9, pp. 1038–1040, 2019, doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-
0224-x. Available: https:// www .nature .com/ articles/ s41587 -019 -0224 -x .
[3] H. Lin, Y. Wu, J. Chen, S. Huang, and Y. Wang, “(−)-4-O-(4-O-‐-D-glucopyranosylcaffeoyl)
Quinic Acid Inhibits the Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells to Enhance the
Efficacy of Anti-PD1 against Colon Cancer,” Pharm Res, vol. 35, no. 9, p. 183, Jul. 2018,
doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2459-5. Available: https:// doi .org/ 10 .1007/ s11095 -018 -2459
-5 .
145