Page 809 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 809
Intercloud and interoperability 5
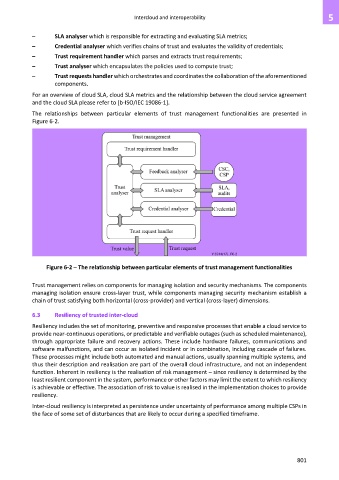
– SLA analyser which is responsible for extracting and evaluating SLA metrics;
– Credential analyser which verifies chains of trust and evaluates the validity of credentials;
– Trust requirement handler which parses and extracts trust requirements;
– Trust analyser which encapsulates the policies used to compute trust;
– Trust requests handler which orchestrates and coordinates the collaboration of the aforementioned
components.
For an overview of cloud SLA, cloud SLA metrics and the relationship between the cloud service agreement
and the cloud SLA please refer to [b-ISO/IEC 19086-1].
The relationships between particular elements of trust management functionalities are presented in
Figure 6-2.
Figure 6-2 – The relationship between particular elements of trust management functionalities
Trust management relies on components for managing isolation and security mechanisms. The components
managing isolation ensure cross-layer trust, while components managing security mechanism establish a
chain of trust satisfying both horizontal (cross-provider) and vertical (cross-layer) dimensions.
6.3 Resiliency of trusted inter-cloud
Resiliency includes the set of monitoring, preventive and responsive processes that enable a cloud service to
provide near-continuous operations, or predictable and verifiable outages (such as scheduled maintenance),
through appropriate failure and recovery actions. These include hardware failures, communications and
software malfunctions, and can occur as isolated incident or in combination, including cascade of failures.
These processes might include both automated and manual actions, usually spanning multiple systems, and
thus their description and realisation are part of the overall cloud infrastructure, and not an independent
function. Inherent in resiliency is the realisation of risk management – since resiliency is determined by the
least resilient component in the system, performance or other factors may limit the extent to which resiliency
is achievable or effective. The association of risk to value is realised in the implementation choices to provide
resiliency.
Inter-cloud resiliency is interpreted as persistence under uncertainty of performance among multiple CSPs in
the face of some set of disturbances that are likely to occur during a specified timeframe.
801