Page 808 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 808
5 Intercloud and interoperability
Appropriate policy language implemented in the trusted inter-cloud environment provides expressiveness
beyond the boundary of access control. This should respect security mechanisms of trust management
systems to fulfil specified requirements.
Trust management in inter-cloud environments (as an interaction enabler in situations of risk and uncertainty)
is considered in cross-provider and cross-layer dimensions. Decisions of the trust management system are
typically taken based on the prediction of cloud computing actors' behaviours and are based on the SLA
established between CSC and CSP or between CSPs. According to particular needs, trust management can
either be CSC-related or CSP-related.
The trust management functionalities are supported by the "Authorisation and security policy management"
functional component within the multi-layer functions of the cloud computing reference architecture
[ITU-T Y.3502]. The positioning of trust management functionalities across the CSPs which provide inter-
cloud services is presented in Figure 6-1.
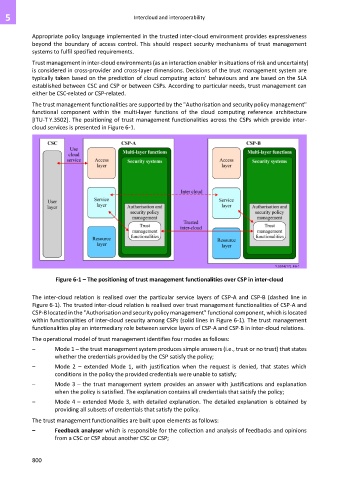
Figure 6-1 – The positioning of trust management functionalities over CSP in inter-cloud
The inter-cloud relation is realised over the particular service layers of CSP-A and CSP-B (dashed line in
Figure 6-1). The trusted inter-cloud relation is realised over trust management functionalities of CSP-A and
CSP-B located in the "Authorisation and security policy management" functional component, which is located
within functionalities of inter-cloud security among CSPs (solid lines in Figure 6-1). The trust management
functionalities play an intermediary role between service layers of CSP-A and CSP-B in inter-cloud relations.
The operational model of trust management identifies four modes as follows:
– Mode 1 – the trust management system produces simple answers (i.e., trust or no trust) that states
whether the credentials provided by the CSP satisfy the policy;
– Mode 2 – extended Mode 1, with justification when the request is denied, that states which
conditions in the policy the provided credentials were unable to satisfy;
– Mode 3 – the trust management system provides an answer with justifications and explanation
when the policy is satisfied. The explanation contains all credentials that satisfy the policy;
– Mode 4 – extended Mode 3, with detailed explanation. The detailed explanation is obtained by
providing all subsets of credentials that satisfy the policy.
The trust management functionalities are built upon elements as follows:
– Feedback analyser which is responsible for the collection and analysis of feedbacks and opinions
from a CSC or CSP about another CSC or CSP;
800