Page 225 - ITU Kaleidoscope 2016
P. 225
ICTs for a Sustainable World
overcome with a long congestion avoidance phase. resource assignment. Following a fair comparison between
NewReno and Illinois behaved very well among different both QoS measurement philosophies and trying to mask
mobility contexts. However, Illinois due to its delay- cross-traffic effects, multiple measurements will be held.
awareness achieved the best performance in regard to the The detection of main features is very important in order to
use of available radio resources. extrapolate those results and analysis to mobile schemes.
Considering the necessity of studying similar effects Second stage will be dedicated to constraint QoS
over real equipment, comparable measurements were measurement by testing them under real mobility patterns.
carried out in the controlled deployment and the To that purpose three main cases will be analyzed:
performance of CCAs (See differences in Figure 8) has 1) Predictable, unstable and low speed mobility pattern
confirmed previous macroscopic behavior findings (both (PULP) – A mobility with multiple stops low average speed
the impact of Hybrid Slow-Start and CCAs’ singularities). and quite defined traffic pattern (for instance buses). This
pattern will be very challenging for both measurement
methodologies for its variability regarding the channel
conditions and the key feature to accomplish the hard work
of measuring will be the responsiveness.
2) Predictable, constant and high speed mobility pattern
(PCHP) - Mobility with straight patterns, higher speeds and
less stops or at least longer gaps between stops (for example
trains). This pattern is very convenient for the analysis of
speed’s impact and how to overcome it in order to get a
proper measurement.
3) Completely unpredictable mobility pattern (CUP) - Very
scattered conditions regarding stops, time of the day and
speed; traffic-dependent (for instance trucks, cars and so
Figure 8. Different CCAs’ performance (Controlled deployment) on). This pattern is not a pattern itself since the
unpredictability and uncertainty is the major characteristic.
All the results involved in this subsection have shown
However, it is very important to have such a challenging
that performing measurements at different stair’s levels help
confirm findings and in the same way, detect impact conditions to be capable of having every imaginable
condition and pattern variability wrapped up in a single day.
differences between the measurement platforms themselves
It will be a fantastic playground for the differentiation of
could provoke.
both measurement methods in which all possible conditions
are folded.
4. MISSING PIECE PROPOSAL: LARGE-SCALE
MEASUREMENT CAMPAIGN The experimentation process should follow our
recommendation regarding the experimental repetition with
Our work misses only one piece and the following the same UE to be fully sure about its reported quality for a
proposal will establish the basis for the definition of it. The certain network condition. The measurements will also
work has to cope with QoS measurements dichotomy to consider our findings regarding Hybrid Slow-Start so as to
push the methods work under real and challenging mobility detect possible deficiencies while using TCP CUBIC
conditions so as to confirm or deny related TCP-related and implementation. It is also highly recommendable to define
radio findings. The only way to fulfill all the needs standard-compliant QoS assessments.
addressed in the analysis of Section 3 in a deployment as
realistic as possible (as remarked in Section 2) is the
experimentation over real-world deployments.
As stated before, there is a clear interest in
standardization and research community in general over the
strengths and weaknesses of each QoS measurement
method. The study should be dedicated towards the
clarification of those uncertainties.
Since there is no development in relation to model-
based measurement code, it is mandatory to create such
required methodology. Both measurement approaches’
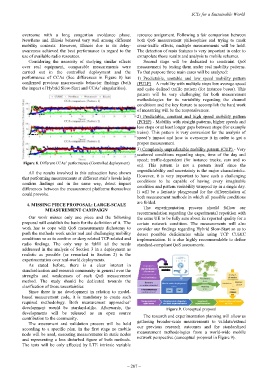
development would be stardard-alike. Afterwards, the Figure 9. Conceptual proposal
developments will be released as an open source
The research and experimentation planning will allow us
contribution to the community.
gathering broader-scale measurements to validate/extend
The assessment and validation process will be held
our previous research outcomes and the standardized
according to a specific plan. In the first stage no mobile
measurement methodologies from a world-wide mobile
node will be used, executing measurements in static nodes
network perspective (conceptual proposal in Figure 9).
and representing a less disturbed figure of both methods.
The tests will be only affected by LTE intrinsic variable
– 207 –