Page 223 - ITU Kaleidoscope 2016
P. 223
ICTs for a Sustainable World
conditions, different UEs could report a different quality It has been demonstrated that there is a need for
and therefore the eNodeB will assign a different MCS for controlling the quality reported by the UE so as to be able
them, enabling in this case higher throughputs with the to assess the impact of it. In the same way, these findings
smartphone. Considering the maximum CQI value being 15, highlight the need for measuring in large-scale deployments
a 3-4 CQI levels difference in average values is a in which the received quality by the UE is more changeable
resounding gap between each other. in accordance with the variability of realistic mobile
We conclude that, even using real UEs huge differences networks.
could appear. For that reason, it is important to perform
experiments with up-to-date UEs and carry out comparative 3.2. Study among the steps of the experimentation stair
studies performing with similar or even same equipment,
This subsection covers the study of precise performance
but also considering that it is difficult to infer from a certain
features among the steps that the experimentation stair
outcome a general-purpose behavior. provides, analyzing them under different experimentation
conditions in order to confirm or deny the resultant
conclusions. The subsection is mainly divided in two TCP-
based research analysis: short and long-term performance.
Firstly, this subsection covers the brief analysis of
TCP’s standard Slow-Start over LTE with an increase of
one packet per acknowledge (ACK) and Hybrid Slow-Start
[25] with the delay-awareness ability to skip earlier in order
to avoid massive packet losses. The following 3 examples
of both methods illustrate their performance in a short-term
with special impact on short-lived flows, thus, on QoS
measurements with a short execution period.
Figure 4 shows in a simulated multi-UE scenario, the
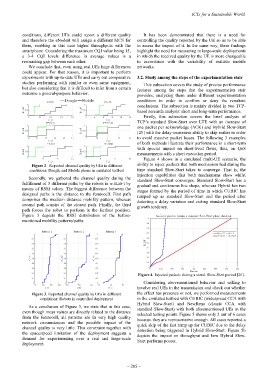
Figure 2. Reported channel quality by UEs in different ability to inject packets that both mechanism had during the
conditions: Dongle and Mobile phone in emulated testbed time standard Slow-Start takes to converge. That is, the
injection capabilities that both mechanisms show whilst
Secondly, we gathered the channel quality during the
standard Slow-Start converges. Standard Slow-Start has a
fulfillment of 3 different paths by the robots in w.iLab-t by
gradual and continuous line shape, whereas Hybrid has two
means of RSSI values. The biggest difference between the
stages formed by the period of time in which CUBIC has
designed paths is the distance to the femtocell. First path
ramped up as standard Slow-Start and the period after
comprises the medium distance mobility pattern, whereas detecting a delay variation and exiting standard Slow-Start
second path consist of the closest path. Finally, the third
growth tendency.
path forces the robot to perform in the furthest position.
Figure 3 depicts the RSSI distribution of the before-
mentioned mobility patterns/paths.
Figure 4. Injected packets during a stand. Slow-Start period [26].
Considering abovementioned behavior and willing to
involve real UEs in the transmission and check out whether
Figure 3. Reported channel quality by UEs in different the effect has presence or not, we performed measurements
conditions: Robots in controlled deployment in the emulated testbed with CUBIC (widespread CCA with
Hybrid Slow-Start) and NewReno (classic CCA with
As a conclusion of Figure 3, we state that in this case,
standard Slow-Start) with both aforementioned UEs in the
even though mean values are directly related to the distance selected testing points. Figure 5 shows only 2 out of 6 cases
from the femtocell, all patterns are in very high quality
because they are representative enough. All cases reported a
network circumstances and the possible impact of the
quick skip of the fast ramp up for CUBIC due to the delay
channel quality is very little. This constraint together with
detection being triggered in Hybrid Slow-Start. Figure 5b
the space/speed limitation of the deployment suggests a depicts the impact on throughput and how Hybrid Slow-
demand for experimenting over a real and large-scale
Start performs poorer.
deployment.
– 205 –