Page 95 - Implementation of ITU-T international standards for sustainable management of waste electrical and electronic equipment: The path to a circular economy in Costa Rica
P. 95
Implementation of ITU-T international standards for sustainable management of waste
electrical and electronic equipment: The path to a circular economy in Costa Rica
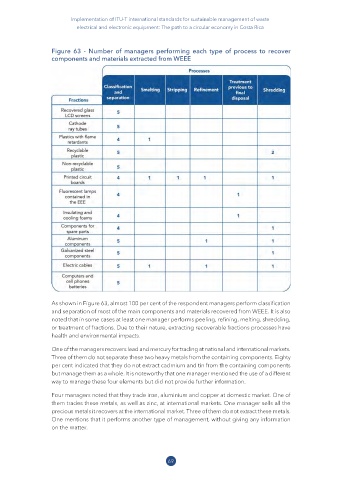
Figure 63 - Number of managers performing each type of process to recover
components and materials extracted from WEEE
As shown in Figure 63, almost 100 per cent of the respondent managers perform classification
and separation of most of the main components and materials recovered from WEEE. It is also
noted that in some cases at least one manager performs peeling, refining, melting, shredding,
or treatment of fractions. Due to their nature, extracting recoverable fractions processes have
health and environmental impacts.
One of the managers recovers lead and mercury for trading at national and international markets.
Three of them do not separate these two heavy metals from the containing components. Eighty
per cent indicated that they do not extract cadmium and tin from the containing components
but manage them as a whole. It is noteworthy that one manager mentioned the use of a different
way to manage these four elements but did not provide further information.
Four managers noted that they trade iron, aluminium and copper at domestic market. One of
them trades these metals, as well as zinc, at international markets. One manager sells all the
precious metals it recovers at the international market. Three of them do not extract these metals.
One mentions that it performs another type of management, without giving any information
on the matter.
69