Page 87 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 7 – Terahertz communications
P. 87
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 7
1400 140
Exp3 10 dB HBA SNR=20dB
Exp3 0 dB HBA SNR=10dB
1200 HBA 0 dB 120 Exp3 SNR=10dB
HBA 10 dB Exp3 SNR=20dB
1000 100
Cumulative regret 800 Cumulative regret 80
600
60
400 40
200 20
0 0
0 50 100 150 200 0 50 100 150 200
Time slots Time slots
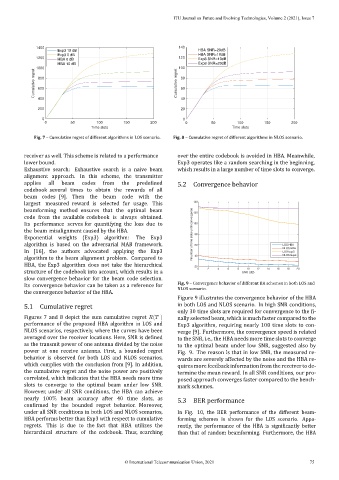
Fig. 7 – Cumulative regret of different algorithms in LOS scenario. Fig. 8 – Cumulative regret of different algorithms in NLOS scenario.
receiver as well. This scheme is related to a performance over the entire codebook is avoided in HBA. Meanwhile,
lower bound. Exp3 operates like a random searching in the beginning,
Exhaustive search: Exhaustive search is a naive beam which results in a large number of time slots to converge.
alignment approach. In this scheme, the transmitter
applies all beam codes from the prede ined 5.2 Convergence behavior
codebook several times to obtain the rewards of all
beam codes [9]. Then the beam code with the
140
largest measured reward is selected for usage. This
beamforming method ensures that the optimal beam 120
code from the available codebook is always obtained.
Its performance serves for quantifying the loss due to 100
the beam misalignment caused by the HBA.
Exponential weights (Exp3) algorithm: The Exp3 Nnumber of time slots untill convergence 80
algorithm is based on the adversarial MAB framework. 60 LOS HBA
In [16], the authors advocated applying the Exp3 NLOS HBA
LOS Exp3
algorithm to the beam alignment problem. Compared to 40 NLOS Exp3
HBA, the Exp3 algorithm does not take the hierarchical 20
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
structure of the codebook into account, which results in a SNR (dB)
slow convergence behavior for the beam code selection.
Fig. 9 – Convergence behavior of different BA schemes in both LOS and
Its convergence behavior can be taken as a reference for
NLOS scenario.
the convergence behavior of the HBA.
Figure 9 illustrates the convergence behavior of the HBA
5.1 Cumulative regret in both LOS and NLOS scenario. In high SNR conditions,
only 30 time slots are required for convergence to the i‑
Figures 7 and 8 depict the sum cumulative regret ( ) nally selected beam, which is much faster compared to the
performance of the proposed HBA algorithm in LOS and Exp3 algorithm, requiring nearly 100 time slots to con‑
NLOS scenarios, respectively, where the curves have been verge [9]. Furthermore, the convergence speed is related
averaged over the receiver locations. Here, SNR is de ined to the SNR, i.e., the HBA needs more time slots to converge
as the transmit power of one antenna divided by the noise to the optimal beam under low SNR, suggested also by
power at one receive antenna. First, a bounded regret Fig. 9. The reason is that in low SNR, the measured re‑
behavior is observed for both LOS and NLOS scenarios, wards are severely affected by the noise and the HBA re‑
which complies with the conclusion from [9]. In addition, quires more feedback information from the receiver to de‑
the cumulative regret and the noise power are positively termine the mean reward. In all SNR conditions, our pro‑
correlated, which indicates that the HBA needs more time posed approach converges faster compared to the bench‑
slots to converge to the optimal beam under low SNR. mark schemes.
However, under all SNR conditions, the HBA can achieve
nearly 100% beam accuracy after 40 time slots, as 5.3 BER performance
con irmed by the bounded regret behavior. Moreover,
under all SNR conditions in both LOS and NLOS scenarios, In Fig. 10, the BER performance of the different beam‑
HBA performs better than Exp3 with respect to cumulative forming schemes is shown for the LOS scenario. Appa-
regrets. This is due to the fact that HBA utilizes the rently, the performance of the HBA is signi icantly better
hierarchical structure of the codebook. Thus, searching than that of random beamforming. Furthermore, the HBA
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 75