Page 48 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 7 – Terahertz communications
P. 48
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 7
1 1 1
Total Total Total
0.9 Dust 0.9 Dust 0.9 Dust
0.8 0.8 0.8
0.7 0.7 0.7
Transmittance 0.5 Transmittance 0.5 Transmittance 0.5
0.6
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.4
0.3 0.3 0.3
0.2 0.2 0.2
0.1 0.1 0.1
0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0 1
10 10 10 10 10 10
Frequency [THz] Frequency [THz] Frequency [THz]
(a) Altitude = 0 km. (b) Altitude =16km. (c) Altitude =30km.
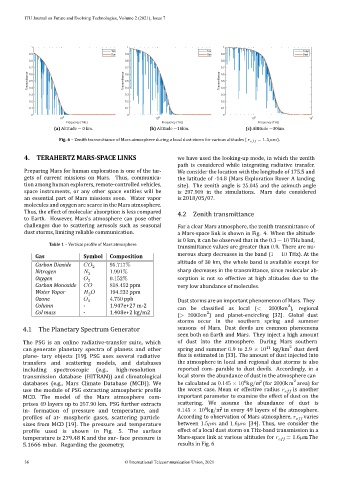
Fig. 6 – Zenith transmittance of Mars atmosphere during a local dust storm for various altitudes ( = 1.5 ).
4. TERAHERTZ MARS‑SPACE LINKS we have used the looking‑up mode, in which the zenith
path is considered while integrating radiative transfer.
Preparing Mars for human exploration is one of the tar‑ We consider the location with the longitude of 175.5 and
gets of current missions on Mars. Thus, communica‑ the latitude of ‑14.8 (Mars Exploration Rover A landing
tion among human explorers, remote‑controlled vehicles, site). The zenith angle is 25.045 and the azimuth angle
space instruments, or any other space entities will be is 297.909 in the simulations. Mars date considered
an essential part of Mars missions soon. Water vapor is 2018/05/07.
molecules and oxygen are scarce in the Mars atmosphere.
Thus, the effect of molecular absorption is less compared
4.2 Zenith transmittance
to Earth. However, Mars’s atmosphere can pose other
challenges due to scattering aerosols such as seasonal For a clear Mars atmosphere, the zenith transmittance of
dust storms, limiting reliable communication. a Mars‑space link is shown in Fig. 4. When the altitude
is 0 km, it can be observed that in the 0.3 − 10 THz band,
Table 1 – Vertical pro ile of Mars atmosphere
transmittance values are greater than 0.9. There are nu‑
Gas Symbol Composition merous sharp decreases in the band (1 − 10 THz). At the
Carbon Dioxide 2 95.717% altitude of 30 km, the whole band is available except for
Nitrogen 2 1.991% sharp decreases in the transmittance, since molecular ab‑
Oxygen 2 0.152% sorption is not so effective at high altitudes due to the
Carbon Monoxide 818.452 ppm very low abundance of molecules.
Water Vapor 194.232 ppm
2
Ozone 3 4.750 ppb Dust storms are an important phenomenon of Mars. They
Column ‑ 1.947e+27 m‑2 can be classi ied as local (< 2000km ), regional
2
Col mass ‑ 1.408e+2 kg/m2 2
(> 2000km ) and planet‑encircling [32]. Global dust
storms occur in the southern spring and summer
4.1 The Planetary Spectrum Generator seasons of Mars. Dust devils are common phenomena
seen both on Earth and Mars. They inject a high amount
The PSG is an online radiative‑transfer suite, which of dust into the atmosphere. During Mars southern
2
can generate planetary spectra of planets and other spring and summer 0.9 to 2.9 × 10 11 kg/km dust devil
plane‑ tary objects [19]. PSG uses several radiative lux is estimated in [33]. The amount of dust injected into
transfers and scattering models, and databases the atmosphere in local and regional dust storms is also
including spectroscopic (e.g., high‑resolution reported com‑ parable to dust devils. Accordingly, in a
transmission database (HITRAN)) and climatological local storm the abundance of dust in the atmosphere can
6 2 2
databases (e.g., Mars Climate Database (MCD)). We be calculated as 0.145 × 10 kg/m (for 2000km area) for
use the module of PSG extracting atmospheric pro ile the worst case. Mean or effective radius is another
MCD. The model of the Mars atmosphere com‑ important parameter to examine the effect of dust on the
prises 49 layers up to 257.90 km. PSG further extracts scattering. We assume the abundance of dust is
6 2
in‑ formation of pressure and temperature, and 0.145 × 10 kg/m in every 49 layers of the atmosphere.
pro iles of at‑ mospheric gases, scattering particle According to observation of Mars atmosphere, varies
sizes from MCD [19]. The pressure and temperature between 1.5 and 1.6 [34]. Thus, we consider the
pro ile used is shown in Fig. 5. The surface effect of a local dust storm on THz‑band transmission in a
temperature is 279.48 K and the sur‑ face pressure is Mars‑space link at various altitudes for = 1.6 m . The
5.1666 mbar. Regarding the geometry, results in Fig. 6
36 © International Telecommunication Union, 2021