Page 75 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 6 – Wireless communication systems in beyond 5G era
P. 75
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 6
4. MULTI‑DOMAINGAMES FRAMEWORK source type ℎ owned by InP that is allocated to MVNO
and , , ≥ 0. We assume, an InP and an MVNO can exer‑
Recently, mathematical economics and business manage‑ cise their Individual Rationality (IR) when , , = 0. In
ment approaches have been employed in designing radio an M‑TTSD network, since an InP can trade its resources
resource management frameworks [7, 66]. To this end, with interested MVNOs, hence
the concepts of FM have played a signi icant role in the
modelling of our M‑TTSD network. Without loss of gen‑ , , ≤ 1, ∀ ∈ ℐ, ∀ℎ ∈ ℋ . (7)
erality, we model an InP ∈ ℐ as a seller, an MVNO ∈ , ∈
and an SP ∈ being buyer/seller depending on the hier‑ An MVNO bids for the resources of an InP taking into
,
archical level in the M‑TTSD network. This is illustrated consideration its resource preference factor Pr . The
in Fig. 4. Following the thesis of FM, we assume, the re‑ resource preference Pr shows the importance of a
, ,ℎ
sources traded in the market are non‑storable and divis‑ particular resource ℎ owned by InP to MVNO . It is
, ,ℎ
ible. For instance, spectrum or bandwidth can be traded of the form given by:
in an M‑TTSD network.
InP 1 InP 2 InP i
Pr = 1, ∀ ∈ ℐ, ∀ ∈ (8)
, ,ℎ
... ℎ ∈ℋ
where Pr , ,ℎ ≥ 0 and with Pr , ,ℎ = 0 indicating that
an MVNO is not interested in a particular resource of an
InP
Seller InP. Moreover, , ≥ 0 and if an MVNO bids , = 0,
MVNO this indicates the MVNO is not interested in bidding for a
Buyers
particular resource. To this end, the price of a resource
... ℎ , of an InP is expressed as:
MVNO 1 MVNO 2 MVNO d
ℎ , = , Pr , ∀ ∈ ℐ, ℎ ∈ ℋ (9)
MVNO , ,ℎ
Sellers ∈
SP Thus, the share of resource ℎ of InP allocated to MVNO
Buyers
is given as:
... ,
, , = Pr , ,ℎ (10)
SP 1 SP 2 SP n ,
Next, we take a close‑up view of the bidding vector of a
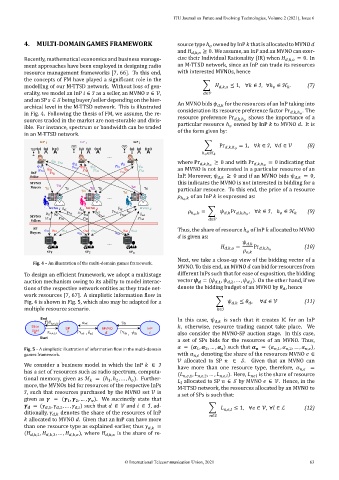
Fig. 4 – An illustration of the multi‑domain games framework.
MVNO. To this end, an MVNO can bid for resources from
To design an ef icient framework, we adopt a multistage different InPs such that for ease of exposition, the bidding
auction mechanism owing to its ability to model interac‑ vector = ( ,1 , ,2 , … , ). On the other hand, if we
,
tions of the respective network entities as they trade net‑ denote the bidding budget of an MVNO by , hence
work resources [7, 67]. A simplistic information low in
Fig. 4 is shown in Fig. 5, which also may be adapted for a , ≤ , ∀ ∈ (11)
multiple resource scenario. ∈ℐ
End In this case, , is such that it creates IC for an InP
Slice SP MVNO InP , otherwise, resource trading cannot take place. We
User
, , also consider the MVNO‑SP auction stage. In this case,
Start
a set of SPs bids for the resources of an MVNO. Thus,
= ( , , … , ) such that = ( , , … , ),
Fig. 5 – A simplistic illustration of information low in the multi‑domain 1 2 ,1 ,2 ,
games framework. with , denoting the share of the resources MVNO ∈
allocated to SP ∈ . Given that an MVNO can
We consider a business model in which the InP ∈ ℐ have more than one resource type, therefore, =
,
has a set of resources such as radio spectrum, computa‑ ( , , … , ). Here, is the share of resource
, ,1
, ,
, ,2
tional memory, given as ℋ = (ℎ , ℎ , … , ℎ ). Further‑ allocated to SP ∈ by MVNO ∈ . Hence, in the
2
1
more, the MVNOs bid for resources of the respective InPs M‑TTSD network, the resources allocated by an MVNO to
ℐ, such that resources purchased by the MVNO set is a set of SPs is such that:
given as = ( , , … , ). We succinctly state that
2
1
= ( ,1 , ,2 , … , ) such that ∈ and ∈ ℐ, ad‑ , , ≤ 1, ∀ ∈ , ∀ ∈ ℒ (12)
,
ditionally, , denotes the share of the resources of InP ∈
allocated to MVNO . Given that an InP can have more
than one resource type as explained earlier, thus , =
( , ,1 , , ,2 , … , , , ), where , , is the share of re‑
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 63