Page 64 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 6 – Wireless communication systems in beyond 5G era
P. 64
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 6
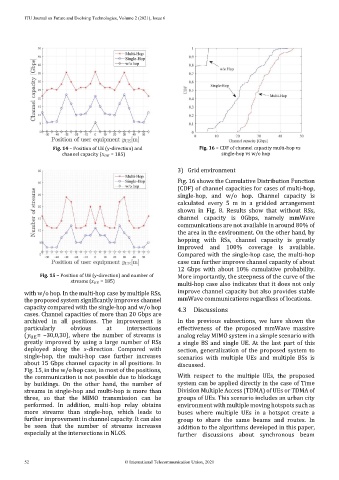
Fig. 14 – Position of UE (y-direction) and Fig. 16 − CDF of channel capacity multi-hop vs
channel capacity ( = 185) single-hop vs w/o hop
3) Grid environment
Fig. 16 shows the Cumulative Distribution Function
(CDF) of channel capacities for cases of multi-hop,
single-hop, and w/o hop. Channel capacity is
calculated every 5 m in a gridded arrangement
shown in Fig. 8. Results show that without RSs,
channel capacity is 0Gbps, namely mmWave
communications are not available in around 80% of
the area in the environment. On the other hand, by
hopping with RSs, channel capacity is greatly
improved and 100% coverage is available.
Compared with the single-hop case, the multi-hop
case can further improve channel capacity of about
12 Gbps with about 10% cumulative probability.
Fig. 15 – Position of UE (y-direction) and number of More importantly, the steepness of the curve of the
streams ( = 185)
multi-hop case also indicates that it does not only
with w/o hop. In the multi-hop case by multiple RSs, improve channel capacity but also provides stable
the proposed system significantly improves channel mmWave communications regardless of locations.
capacity compared with the single-hop and w/o hop 4.3 Discussions
cases. Channel capacities of more than 20 Gbps are
archived in all positions. The improvement is In the previous subsections, we have shown the
particularly obvious at intersections effectiveness of the proposed mmWave massive
( UE = −30,0,30), where the number of streams is analog relay MIMO system in a simple scenario with
greatly improved by using a large number of RSs a single BS and single UE. At the last part of this
deployed along the x-direction. Compared with section, generalization of the proposed system to
single-hop, the multi-hop case further increases scenarios with multiple UEs and multiple BSs is
about 15 Gbps channel capacity in all positions. In discussed.
Fig. 15, in the w/o hop case, in most of the positions,
the communication is not possible due to blockage With respect to the multiple UEs, the proposed
by buildings. On the other hand, the number of system can be applied directly in the case of Time
streams in single-hop and multi-hop is more than Division Multiple Access (TDMA) of UEs or TDMA of
three, so that the MIMO transmission can be groups of UEs. This scenario includes an urban city
performed. In addition, multi-hop relay obtains environment with multiple moving hotspots such as
more streams than single-hop, which leads to buses where multiple UEs in a hotspot create a
further improvement in channel capacity. It can also group to share the same beams and routes. In
be seen that the number of streams increases addition to the algorithms developed in this paper,
especially at the intersections in NLOS. further discussions about synchronous beam
52 © International Telecommunication Union, 2021