Page 21 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 6 – Wireless communication systems in beyond 5G era
P. 21
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 6
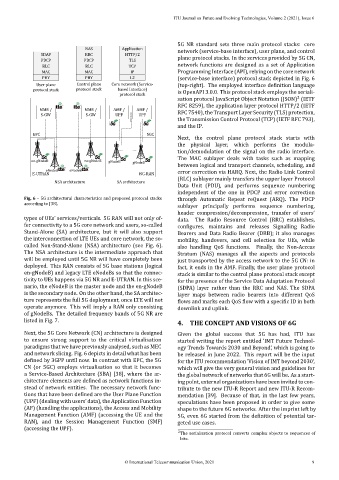
5G NR standard sets three main protocol stacks: core
NAS Application
SDAP RRC HTTP/2 network (service‐base interface), user plane, and control
PDCP PDCP TLS plane protocol stacks. In the services provided by 5G CN,
RLC RLC TCP network functions are designed as a set of Application
MAC MAC IP Programming Interface (API), relying on the core network
PHY PHY L2 (service‐base interface) protocol stack depicted in Fig. 6
User plane Control plane Core network (Service- (top‐right). The employed interface de inition language
protocol stack protocol stack based Interface) is OpenAPI 3.0.0. This protocol stack employs the seriali‐
protocol stack
2
sation protocol JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) (IETF
RFC 8259), the application layer protocol HTTP/2 (IETF
MME / MME / AMF / AMF /
S-GW S-GW UPF UPF RFC 7540), the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protection,
the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) (IETF RFC 793),
and the IP.
EPC 5GC
Next, the control plane protocol stack starts with
the physical layer, which performs the modula‐
tion/demodulation of the signal on the radio interface.
en-gNodeB en-gNodeB gNodeB gNodeB The MAC sublayer deals with tasks such as mapping
between logical and transport channels, scheduling, and
eNodeB eNodeB
E-UTRAN NG-RAN error correction via HARQ. Next, the Radio Link Control
NSA architecture SA architecture (RLC) sublayer mainly transfers the upper layer Protocol
Data Unit (PDU), and performs sequence numbering
independent of the one in PDCP and error correction
Fig. 6 – 5G architectural characteristics and proposed protocol stacks through Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ). The PDCP
according to [38].
sublayer principally performs sequence numbering,
header compression/decompression, transfer of users’
types of UEs’ services/verticals. 5G RAN will not only of‐ data. The Radio Resource Control (RRC) establishes,
fer connectivity to a 5G core network and users, so‐called igures, maintains and releases Signalling Radio
Stand‐Alone (SA) architecture, but it will also support Bearers and Data Radio Bearer (DRB); it also manages
the interconnection of L TE UEs and core network, the so‐ mobility, handovers, and cell selection for UEs, while
called Non‐Stand‐Alone (NSA) architecture (see Fig. 6). also handling QoS functions. Finally, the Non‐Access
The NSA architecture is the intermediate approach that
Stratum (NAS) manages all the aspects and protocols
will be employed until 5G NR will have completely been
just transported by the access network to the 5G CN: in
deployed. This RAN consists of 5G base stations (logical fact, it ends in the AMF. Finally, the user plane protocol
en‐gNodeB) and legacy L TE eNodeBs so that the connec‐ stack is similar to the control plane protocol stack except
tivity to UEs happens via 5G NR and E‐UTRAN. In this sce‐ for the presence of the Service Data Adaptation Protocol
nario, the eNodeB is the master node and the en‐gNodeB (SDPA) layer rather than the RRC and NAS. The SDPA
is the secondary node. On the other hand, the SA architec‐ layer maps between radio bearers into different QoS
ture represents the full 5G deployment, once L TE will not lows and marks each QoS low with a speci ic ID in both
operate anymore. This will imply a RAN only consisting downlink and uplink.
of gNodeBs. The detailed frequency bands of 5G NR are
listed in Fig. 7. 4. THE CONCEPT AND VISIONS OF 6G
Next, the 5G Core Network (CN) architecture is designed Given the global success that 5G has had, ITU has
to ensure strong support to the critical virtualisation started writing the report entitled ’IMT Future Technol‐
paradigms that we have previously analysed, such as MEC ogy Trends Towards 2030 and Beyond’, which is going to
and network slicing. Fig. 6 depicts in detail what has been be released in June 2022. This report will be the input
de ined by 3GPP until now. In contrast with EPC, the 5G for the ITU recommendation ’Vision of IMT beyond 2030’,
CN (or 5GC) employs virtualisation so that it becomes which will give the very general vision and guidelines for
a Service‐Based Architecture (SBA) [38], where the ar‐ the global network of networks that 6G will be. As a start‐
chitecture elements are de ined as network functions in‐ ing point, external organizations have been invited to con‐
stead of network entities. The necessary network func‐ tribute to the new ITU‐R Report and new ITU‐R Recom‐
tions that have been de ined are the User Plane Function mendation [39]. Because of that, in the last few years,
(UPF) (dealing with users’ data), the Application Function speculations have been proposed in order to give some
(AF) (handling the applications), the Access and Mobility shape to the future 6G networks. After the imprint left by
Management Function (AMF) (accessing the UE and the 5G, even 6G started from the de inition of potential tar‐
RAN), and the Session Management Function (SMF) geted use cases.
(accessing the UPF).
2 The serialisation protocol converts complex objects to sequences of
bits.
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 9