Page 15 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5 – Internet of Everything
P. 15
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5
perform edge resource allocation. Similarly, the auction
theory t pr it pro it
[36 which nov optimal and
data allocation problem is solved with the Bayesian auc‑
tion appr The pro it maximization in the cognitive
virtual operator is addressed in paper [37], in which a dy‑
namic network scenario is consider Paper [37] devel‑
ops a low complexity online control scheme to perform
decisions about price and resource planning. A cloud allo‑
cation scheme for three classes of virtual machines is pre‑
sented in [38], with the aim of maximising cloud provider
pro it.
Recently FL has gained attention and papers [8 39 40,
41 42 20 provide application t differ contexts
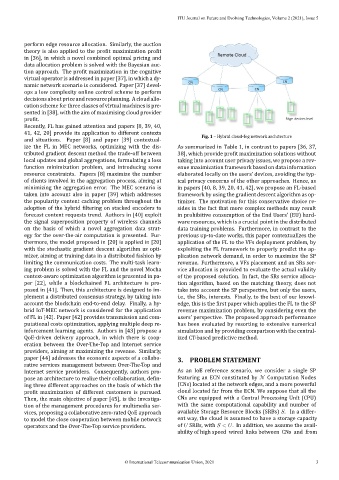
Fig. 1 – Hybrid cloud‑fog network architecture
P [8 [39 contextual‑
ize FL network dis‑ As summarized in Table 1, in contrast to papers [36, 37,
tributed gradient descent method the trade‑off between 38], which provide pro it maximization solutions without
local updates and global aggregations, formulating a loss taking into account user privacy issues, we propose a rev‑
pr intr some enue maximization framework based on data information
resour constr Papers [8 number elaborated locally on the users’ devices, avoiding the typ‑
of clients involved in the aggregation process, aiming at ical privacy concerns of the other approaches. Hence, as
minimizing aggreg error The scenario is in papers [40, 8, 39, 20, 41, 42], we propose an FL‑based
tak int account [39 which addresses framework by using the gradient descent algorithm as op‑
popularity cont pr throug the timizer. The motivation for this conservative choice re‑
of hybrid iltering stacked encoders to sides in the fact that more complex methods may result
forecast content requests tr Authors in [40] exploit in prohibitive consumption of the End Users’ (EU) hard‑
signal superposition pr of wireless channels ware resources, which is a crucial point in the distributed
of which nov aggreg data strat‑ data training problems. Furthermore, in contrast to the
egy for the over‑the‑air computation is present Fur‑ previous up‑to‑date works, this paper contextualizes the
thermore, the model proposed in [20] is applied in [20] application of the FL to the VFs deployment problem, by
stochastic gr descent opti‑ exploiting the FL framework to properly predict the ap‑
mizer, aiming at training data in a distributed fashion by plication network demand, in order to maximize the SP
limiting the communication costs. The multi‑task learn‑ revenue. Furthermore, a VFs placement and an SRs ser‑
pr solved FL nov Mocha vice allocation is provided to evaluate the actual validity
context‑aware optimization algorithm is presented in pa‑ of the proposed solution. In fact, the SRs service alloca‑
per [22 w blockchained FL architectur pro‑ tion algorithm, based on the matching theory, does not
posed in [41 Then, this architecture is designed to im‑ take into account the SP perspective, but only the users,
plement a distributed consensus strategy, by taking into i.e., the SRs, interests. Finally, to the best of our knowl‑
account block end‑to‑end delay Finally hy‑ edge, this is the irst paper which applies the FL to the SP
brid IoT‑MEC networ consider for application revenue maximization problem, by considering even the
of FL in [42]. Paper [42] provides transmission and com‑ users’ perspective. The proposed approach performance
putational costs optimization, applying multiple deep re‑ has been evaluated by resorting to extensive numerical
inforcement learning Authors in [43] propose a simulation and by providing comparison with the central‑
QoE‑driv delivery appr which ther coop‑ ized CT‑based predictive method.
er betw Over‑The‑T Int service
providers, aiming at maximizing the rev Similarly,
paper [44] addresses the economic aspects of a collabo‑ 3. PROBLEM STATEMENT
rativ services management betw Over‑The‑T and
Int service providers. Consequently pro‑ As an IoE reference scenario, we consider a single SP
pose an architecture to realize their collaboration, de in‑ featuring an ECN constituted by Computation Nodes
ing three different approaches on the basis of which the (CNs) located at the network edges, and a more powerful
pr it of differ customers pursued. cloud located far from the ECN. We suppose that all the
Then, the main objective of paper [45 is the investiga‑ CNs are equipped with a Central Processing Unit (CPU)
tion of the management procedures for multimedia ser‑ with the same computational capability and number of
vices, proposing a collaborative zero‑rated QoE approach available Storage Resource Blocks (SRBs) . In a differ‑
to model the close cooperation between mobile network ent way, the cloud is assumed to have a storage capacity
operators and the Over‑The‑Top service providers. of SRBs, with < . In addition, we assume the avail‑
ability of high speed wired links between CNs and from
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 3