Page 111 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5 – Internet of Everything
P. 111
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5
number of processes. Each base station consists of M value is usually given by the manufacturer of the
central processing unit(s), and memory units the CPU and it is unique to CPU model, type, and family.
power consumption of which increases with the When a certain percentage of a base station’s
increasing amount of load. Increasing power resources is assigned to the mining process, BCR
consumption also increases the heat on the device, will increase since miner base stations will only use
which in turn decreases the processing capability of these resources to create a block in small-cell
the device. blockchain. LTDS depends on the type of the link
changing between (1msec., 10 msec.). With an
increasing number of nodes, BCR also increases.
The VUPU transaction rate will decrease which is
not acceptable since a fast VUPU transaction record
rate should be very fast so that buy and sell orders
can be executed in almost real time. On the contrary,
bigger N values will lead to a higher VUPU value.
With one cluster head in a network cluster with
100 base stations each with a single processor, with
TDF = 2.5, the BCR is calculated as follows:
( 1 )
Fig. 12 – Network cluster message exchange model = (2 100 10 ) + ( 2.5 ) =
One proposed model for BPS is 2 sec + 40 = 2.04 . (13)
1
) + C (12)
= ( ) . ( (log 10 ( )) By changing the cluster size, base station type,
transmission link type between base stations, BCR
where ‘a’ is the number of processors of base station can be changed, adjusted and be made location and
hardware, or number of cores in a single processor. time dependent.
‘V’ is the number of processes, threads processed by
hardware of the base station and ‘C’ is the number 5. CONCLUSION
of processors or processor cores assigned to the
mining process. This paper presented a novel blockchain-based
tokenization method for wireless network
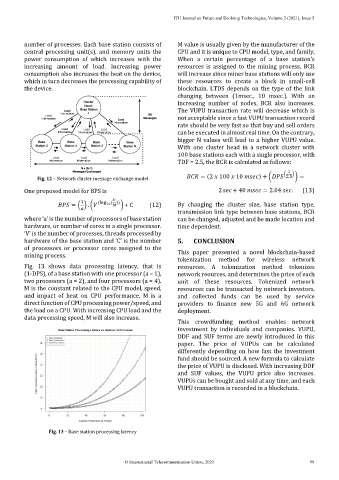
Fig. 13 shows data processing latency, that is resources. A tokenization method tokenizes
(1-DPS), of a base station with one processor (a = 1), network reources, and determines the price of each
two processors (a = 2), and four processors (a = 4). unit of these resources. Tokenized network
M is the constant related to the CPU model, speed, resources can be transacted by network investors,
and impact of heat on CPU performance. M is a and collected funds can be used by service
direct function of CPU processing power/speed, and providers to finance new 5G and 6G network
the load on a CPU. With increasing CPU load and the deployment.
data processing speed, M will also increase.
This crowdfunding method enables network
investment by individuals and companies. VUPU,
DDF and SUF terms are newly introduced in this
paper. The price of VUPUs can be calculated
differently depending on how fast the investment
fund should be sourced. A new formula to calculate
the price of VUPU is disclosed. With increasing DDF
and SUF values, the VUPU price also increases.
VUPUs can be bought and sold at any time, and each
VUPU transaction is recorded in a blockchain.
Fig. 13 – Base station processing latency
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 99