Page 109 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5 – Internet of Everything
P. 109
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 5
3. BLOCKCHAIN
3.1 What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that
records transactions securely in an untrusted
system [2], [13]. Blockchain records each
transaction as a part of an existing block or as a new
block. The first block in a blockchain is called the
genesis block, and this is where blockchain starts.
Each block generates encrypted input to the next
block, and this creates extremely secure chains of
blocks, where one unauthorized change in a block
will make all blocks invalid [2], [12-13].
Each block in a blockchain is generated by a group
of computing nodes called miners [2]. Miners
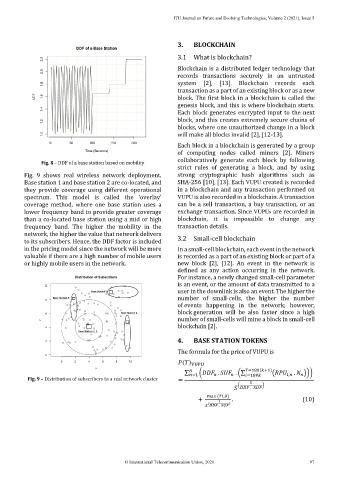
Fig. 8 – DDF of a base station based on mobility collaboratively generate each block by following
strict rules of generating a block, and by using
Fig. 9 shows real wireless network deployment. strong cryptographic hash algorithms such as
Base station 1 and base station 2 are co-located, and SHA-256 [10], [13]. Each VUPU created is recorded
they provide coverage using different operational in a blockchain and any transaction performed on
spectrum. This model is called the ‘overlay’ VUPU is also recorded in a blockchain. A transaction
coverage method, where one base station uses a can be a sell transaction, a buy transaction, or an
lower frequency band to provide greater coverage exchange transaction. Since VUPUs are recorded in
than a co-located base station using a mid or high blockchain, it is impossible to change any
frequency band. The higher the mobility in the transaction details.
network, the higher the value that network delivers
to its subscribers. Hence, the DDF factor is included 3.2 Small-cell blockchain
in the pricing model since the network will be more In a small-cell blockchain, each event in the network
valuable if there are a high number of mobile users is recorded as a part of an existing block or part of a
or highly mobile users in the network. new block [2], [12]. An event in the network is
defined as any action occurring in the network.
For instance, a newly changed small-cell parameter
is an event, or the amount of data transmitted to a
user in the downlink is also an event. The higher the
number of small-cells, the higher the number
of events happening in the network; however,
block generation will be also faster since a high
number of small-cells will mine a block in small-cell
blockchain [2].
4. BASE STATION TOKENS
The formula for the price of VUPU is
( ) VUPU
∑ ( . . (∑ =180( +1) ( . )))
Fig. 9 – Distribution of subscribers In a real network cluster = =1 =180 ,
( 1 )
.
max { ,0}
+ 1 . (10)
(
. )
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 97