Page 119 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3 – Internet of Bio-Nano Things for health applications
P. 119
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3
Table 1 – Model and simulation parameters
Parameter Value Unit Symbol
Speci ic forward resistance 100 [26] Ω
6
Speci ic leakage resistance 10 [26] Ω 2
Speci ic membrane leakage capacitance 10 −2 [26] −2
Axolemma thickness 5 × 10 −9 [27]
Length of myelinated segment 1 × 10 −3 [28]
Length of paranodal region 1 × 10 −4 [21]
Axon radius 10 −5 [21]
Myelin turn number 20 [29]
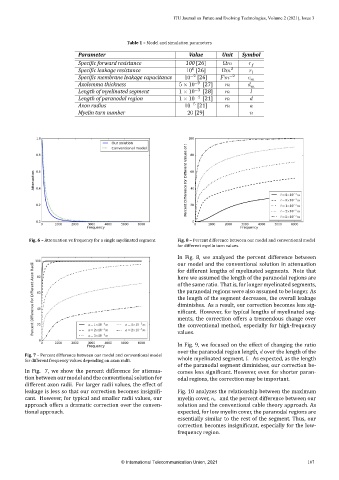
Fig. 6 – Attenuation vs frequency for a single myelinated segment. Fig. 8 – Percent difference between our model and conventional model
for different myelin turn values.
between
our model and the conventional solution in attenuation
for different lengths of myelinated segments. Note that
here we assumed the length of the paranodal regions are
of the same ratio. That is, for longer myelinated segments,
the paranodal regions were also assumed to be longer. As
the length of the segment decreases, the overall leakage
diminishes. As a result, our correction becomes less sig‑
icant. However, for typical lengths of myelinated seg‑
ments, the correction offers a tremendous change over
the conventional method, especially for high‑frequency
values.
In Fig. 9, we focused on the effect of changing the ratio
over the paranodal region length, over the length of the
Fig. 7 – Percent difference between our model and conventional model
for different frequency values depending on axon radii. whole myelinated segment, . As expected, as the length
of the paranodal segment diminishes, our correction be‑
In Fig. 7, we show the percent difference for attenua‑ comes less icant. However, even for shorter paran‑
tion between our model and the conventional solution for odal regions, the correction may be important.
different axon radii. For larger radii values, the effect of
leakage is less so that our correction becomes insigni i‑ Fig. 10 analyzes the relationship between the maximum
cant. However, for typical and smaller radii values, our myelin cover, , and the percent difference between our
approach offers a dramatic correction over the conven‑ solution and the conventional cable theory approach. As
tional approach. expected, for low myelin cover, the paranodal regions are
essentially similar to the rest of the segment. Thus, our
correction becomes insigni icant, especially for the low‑
frequency region.
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 107