Page 31 - FIGI Digital Financial Services security assurance framework
P. 31
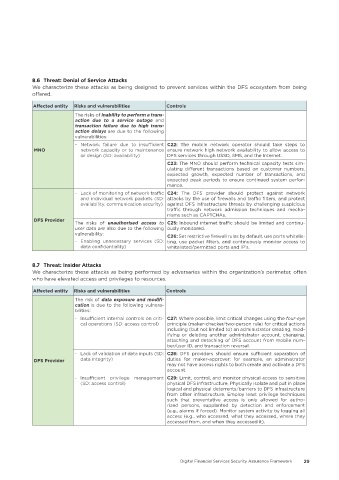
8�6 Threat: Denial of Service Attacks
We characterize these attacks as being designed to prevent services within the DFS ecosystem from being
offered.
Affected entity Risks and vulnerabilities Controls
The risks of inability to perform a trans-
action due to a service outage and
transaction failure due to high trans-
action delays are due to the following
vulnerabilities:
- Network failure due to insufficient C22: The mobile network operator should take steps to
MNO network capacity or to maintenance ensure network high network availability to allow access to
or design (SD: availability) DFS services through USSD, SMS, and the Internet.
C23: The MNO should perform technical capacity tests sim-
ulating different transactions based on customer numbers,
expected growth, expected number of transactions, and
expected peak periods to ensure continued system perfor-
mance.
- Lack of monitoring of network traffic C24: The DFS provider should protect against network
and individual network packets (SD: attacks by the use of firewalls and traffic filters, and protect
availability, communication security) against DFS infrastructure threats by challenging suspicious
traffic through network admission techniques and mecha-
nisms such as CAPTCHAs.
DFS Provider
The risks of unauthorised access to C25: Inbound internet traffic should be limited and continu-
user data are also due to the following ously monitored.
vulnerability: C26: Set restrictive firewall rules by default, use ports whitelis-
- Enabling unnecessary services (SD: ting, use packet filters, and continuously monitor access to
data confidentiality) whitelisted/permitted ports and IP's.
8�7 Threat: Insider Attacks
We characterize these attacks as being performed by adversaries within the organization’s perimeter, often
who have elevated access and privileges to resources.
Affected entity Risks and vulnerabilities Controls
The risk of data exposure and modifi-
cation is due to the following vulnera-
bilities:
- Insufficient internal controls on criti- C27: Where possible, limit critical changes using the four-eye
cal operations (SD: access control) principle (maker-checker/two-person rule) for critical actions
including (but not limited to) an administrator creating, mod-
ifying or deleting another administrator account, changing,
attaching and detaching of DFS account from mobile num-
ber/user ID, and transaction reversal.
- Lack of validation of data inputs (SD: C28: DFS providers should ensure sufficient separation of
DFS Provider data integrity) duties for maker-approver; for example, an administrator
may not have access rights to both create and activate a DFS
account.
- Insufficient privilege management C29: Limit, control, and monitor physical access to sensitive
(SD: access control) physical DFS infrastructure. Physically isolate and put in place
logical and physical deterrents/barriers to DFS infrastructure
from other infrastructure. Employ least privilege techniques
such that preventative access is only allowed for autho-
rized persons, supplanted by detection and enforcement
(e.g., alarms if forced). Monitor system activity by logging all
access (e.g., who accessed, what they accessed, where they
accessed from, and when they accessed it).
Digital Financial Services Security Assurance Framework 29