Page 96 - ITU Journal, ICT Discoveries, Volume 3, No. 1, June 2020 Special issue: The future of video and immersive media
P. 96
ITU Journal: ICT Discoveries, Vol. 3(1), June 2020
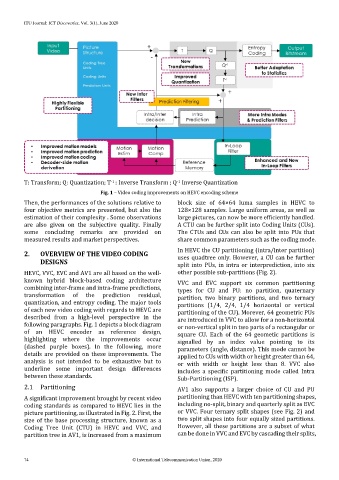
T: Transform; Q: Quantization; T : Inverse Transform ; Q Inverse Quantization
-1
-1
Fig. 1 – Video coding improvements on HEVC encoding scheme
Then, the performances of the solutions relative to block size of 64×64 luma samples in HEVC to
four objective metrics are presented, but also the 128×128 samples. Large uniform areas, as well as
estimation of their complexity . Some observations large pictures, can now be more efficiently handled.
are also given on the subjective quality. Finally A CTU can be further split into Coding Units (CUs).
some concluding remarks are provided on The CTUs and CUs can also be split into PUs that
measured results and market perspectives. share common parameters such as the coding mode.
In HEVC the CU partitioning (intra/inter partition)
2. OVERVIEW OF THE VIDEO CODING uses quadtree only. However, a CU can be further
DESIGNS split into PUs, in intra or interprediction, into six
HEVC, VVC, EVC and AV1 are all based on the well- other possible sub-partitions (Fig. 2).
known hybrid block-based coding architecture VVC and EVC support six common partitioning
combining inter-frame and intra-frame predictions, types for CU and PU: no partition, quaternary
transformation of the prediction residual, partition, two binary partitions, and two ternary
quantization, and entropy coding. The major tools partitions (1/4, 2/4, 1/4 horizontal or vertical
of each new video coding with regards to HEVC are partitioning of the CU). Morever, 64 geometric PUs
described from a high-level perspective in the are introduced in VVC to allow for a non-horizontal
following paragraphs. Fig. 1 depicts a block diagram or non-vertical split in two parts of a rectangular or
of an HEVC encoder as reference design, square CU. Each of the 64 geometic partitions is
highlighting where the improvements occur signalled by an index value pointing to its
(dashed purple boxes). In the following, more parameters (angle, distance). This mode cannot be
details are provided on these improvements. The applied to CUs with width or height greater than 64,
analysis is not intended to be exhaustive but to or with width or height less than 8. VVC also
underline some important design differences includes a specific partitioning mode called Intra
between these standards. Sub-Partitioning (ISP).
2.1 Partitioning AV1 also supports a larger choice of CU and PU
A significant improvement brought by recent video partitioning than HEVC with ten partitioning shapes,
coding standards as compared to HEVC lies in the including no-split, binary and quarterly split as EVC
picture partitioning, as illustrated in Fig. 2. First, the or VVC. Four ternary split shapes (see Fig. 2) and
size of the base processing structure, known as a two split shapes into four equally sized partitions.
Coding Tree Unit (CTU) in HEVC and VVC, and However, all these partitions are a subset of what
partition tree in AV1, is increased from a maximum can be done in VVC and EVC by cascading their splits,
74 © International Telecommunication Union, 2020