Page 143 - ITU Journal, Future and evolving technologies - Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1, Inaugural issue
P. 143
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1
Flexibility
Infancy Stage of Evolved Stage of
Infancy Stage of Evolved Stage of Infancy Stage of Evolved Stage of Flexible
Cellular Cellular High Speed High Speed Flexible
Communications Communications Data Rates Data Rates Communications Communications
Platform Platform
Only Essential Rules Only Essential Rules
Standard Defined - Standard Defined - Standard Defined - Standard Defined -
Transmitter Standard Defined - Standard Defined -
No Flexibility Low Flexibility Medium Flexibility High Flexibility
Very High Flexibility Ultra Flexibility
Channel Random Random Random Random Random Controlled
Intentionally Created Intentionally Created
Interference Avoided Avoided Controlled Controlled
and Controlled and Controlled
Receiver No Flexibility Low Flexibility Medium Flexibility High Flexibility Very High Flexibility Ultra Flexibility
Generations
1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G
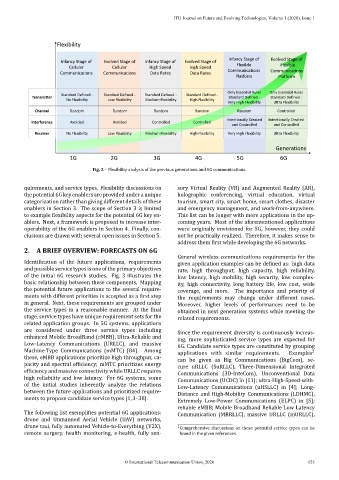
Fig. 2 – Flexibility analysis of the previous generations and 6G communications.
quirements, and service types. Flexibility discussions on sory Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR),
the potential 6G key enablers are provided under a unique holographic conferencing, virtual education, virtual
categorization rather than giving different details of these tourism, smart city, smart home, smart clothes, disaster
enablers in Section 3. The scope of Section 3 is limited and emergency management, and work-from-anywhere.
to example lexibility aspects for the potential 6G key en- This list can be longer with more applications in the up-
ablers. Next, a framework is proposed to increase inter- coming years. Most of the aforementioned applications
operability of the 6G enablers in Section 4. Finally, con- were originally envisioned for 5G, however, they could
clusions are drawn with several open issues in Section 5. not be practically realized. Therefore, it makes sense to
address them irst while developing the 6G networks.
2. A BRIEF OVERVIEW: FORECASTS ON 6G
General wireless communications requirements for the
Identi ication of the future applications, requirements given application examples can be de ined as: high data
and possible service types is one of the primary objectives rate, high throughput, high capacity, high reliability,
of the initial 6G research studies. Fig. 3 illustrates the low latency, high mobility, high security, low complex-
basic relationship between these components. Mapping ity, high connectivity, long battery life, low cost, wide
the potential future applications to the several require- coverage, and more. The importance and priority of
ments with different priorities is accepted as a irst step the requirements may change under different cases.
in general. Next, these requirements are grouped under Moreover, higher levels of performances need to be
the service types in a reasonable manner. At the inal obtained in next generation systems while meeting the
stage, service types have unique requirement sets for the related requirements.
related application groups. In 5G systems, applications
are considered under three service types including Since the requirement diversity is continuously increas-
enhanced Mobile BroadBand (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable and ing, more sophisticated service types are expected for
Low-Latency Communications (URLLC), and massive 6G. Candidate service types are constituted by grouping
Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) [84]. Among applications with similar requirements. Examples 2
these, eMBB applications prioritize high throughput, ca- can be given as Big Communications (BigCom), se-
pacity and spectral ef iciency; mMTC prioritizes energy cure uRLLC (SuRLLC), Three-Dimensional Integrated
ef iciency and massive connectivity while URLLC requires Communications (3D-InteCom), Unconventional Data
high reliability and low latency. For 6G systems, some Communications (UCDC) in [11]; ultra-High-Speed-with-
of the initial studies inherently analyze the relations Low-Latency Communications (uHSLLC) in [4]; Long-
between the future applications and prioritized require- Distance and High-Mobility Communications (LDHMC),
ments to propose candidate service types [1,3–38]. Extremely Low-Power Communications (ELPC) in [5];
reliable eMBB; Mobile Broadband Reliable Low Latency
The following list exempli ies potential 6G applications: Communication (MBRLLC), massive URLLC (mURLLC),
drone and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) networks,
drone taxi, fully automated Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X), 2 Comprehensive discussions on these potential service types can be
remote surgery, health monitoring, e-health, fully sen- found in the given references.
© International Telecommunication Union, 2020 123