Page 142 - ITU Journal, Future and evolving technologies - Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1, Inaugural issue
P. 142
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1
Features/ Generations 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G
EDGE 8PSK
GSM GMSK
CDMA 2000 QPSK, OQPSK BPSK
BPSK, QPSK,
Modulation FM W-CDMA QPSK, OQPSK QPSK NR 16QAM, 64QAM,
Options 16 QAM 256QAM
GPRS GMSK UMTS QPSK 64 QAM
HSDPA QPSK, 16 QAM
Convolutional Coding Turbo Coding Turbo Coding LDPC
Coding
Block Coding
Options Block Coding Convolutional Coding Convolutional Coding
Polar Coding
Modulation and Coding
Fixed Limited MCS Options Medium MCS Options High MCS Options
Scheme (MCS) Options
Fixed Lattice Fixed Lattice Fixed Lattice Adaptive Lattice
Adaptive
Waveform Fixed Shape (GMSK) Fixed Shape (RC) Windowing and Filtering Windowing and Filtering
Options Uplink SC-FDE Uplink OFDM, SC-FDE
Fixed Type (The same for uplink Fixed Type (The same for uplink
and downlink) and downlink)
Downlink OFDM Downlink OFDM
Multiple Accessing Uplink SC-FDMA Uplink SC-FDMA
Options FDMA TDMA CDMA Downlink OFDMA Downlink OFDMA
Carrier Frequency AMPS 800 MHz 900 MHz 800 MHz 600 MHz microWave 600 MHz – 6 GHz
–
-
Options microWave microWave GSM microWave 2.1 GHz microWave 2.5 GHz
NMT 450 MHz 1800 MHz mmWave 6 GHz – 300 GHz
Architecture Options SISO SISO SISO MIMO mMIMO
Frequency Reuse – 1 Frequency Reuse – 1
Cell Planning Frequency Reuse – 7 Frequency Reuse – 3, 4, 7, 12 Frequency Reuse – 1 Fractional Frequency Reuse Fractional Frequency Reuse
Soft Frequency Reuse Soft Frequency Reuse
ICIC COMP
User-Cell Association Mobile-assisted Hand-off Soft Hand-off CRAN
Options Attempt to COMP
Small Cell
Freq. Multi-User Diversity
Multi-User
Freq.
Freq. Frequency Hopping Freq. FHSS Diversity Space MIMO
Diversity Space MIMO Space Precoding
Options Space Precoding
Space Beamforming
Time Path Diversity Time DSSS
Space Beamforming Space COMP
Receiver Types Multi-tap TDE Rake Receiver A Single Tap FDE A Single Tap FDE
GSM 200KHz (8 slots) CDMA 1.25 MHz 1.25 MHz to 20 MHz BWP
Carrier Aggregation
Bandwidth DAMPS 30KHz (3 slots) WCDMA 5MHz
Options AMPS 30 kHz 100 MHz with Carrier Multi-numerology
PDC
25KHz (3 slots) TD-SCDMA 1.6MHz Aggregation License Assisted Access (LAA)
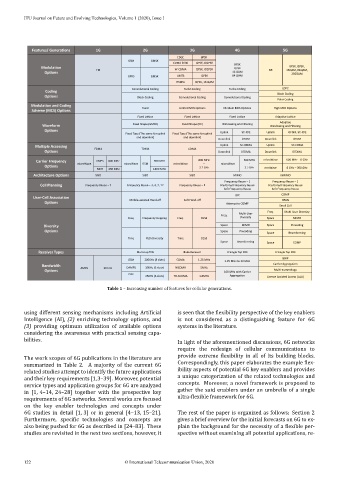
Table 1 – Increasing number of features for cellular generations.
using different sensing mechanisms including Arti icial is seen that the lexibility perspective of the key enablers
Intelligence (AI), (2) enriching technology options, and is not considered as a distinguishing feature for 6G
(3) providing optimum utilization of available options systems in the literature.
considering the awareness with practical sensing capa-
bilities. In light of the aforementioned discussions, 6G networks
require the redesign of cellular communications to
The work scopes of 6G publications in the literature are provide extreme lexibility in all of its building blocks.
summarized in Table 2. A majority of the current 6G Correspondingly, this paper elaborates the example lex-
related studies attempt to identify the future applications ibility aspects of potential 6G key enablers and provides
and their key requirements [1,3–39]. Moreover, potential a unique categorization of the related technologies and
service types and application groups for 6G are analyzed concepts. Moreover, a novel framework is proposed to
in [1, 4–14, 24–28] together with the prospective key gather the said enablers under an umbrella of a single
requirements of 6G networks. Several works are focused ultra- lexible framework for 6G.
on the key enabler technologies and concepts under
6G studies in detail [1, 3] or in general [4–13, 15–21]. The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2
Furthermore, speci ic technologies and concepts are gives a brief overview for the initial forecasts on 6G to ex-
also being pushed for 6G as described in [24–83]. These plain the background for the necessity of a lexible per-
studies are revisited in the next two sections, however, it spective without examining all potential applications, re-
122 © International Telecommunication Union, 2020