Page 13 - Methodology for inter-operator and cross-border P2P money transfers
P. 13
7 CONVENTIONS
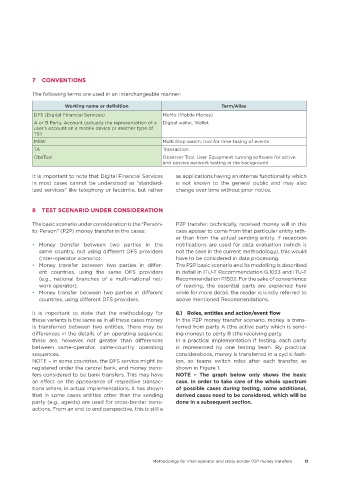
The following terms are used in an interchangeable manner:
Working name or definition Term/Alias
DFS (Digital Financial Services) MoMo (Mobile Money)
A or B Party, Account (actually the representation of a Digital wallet, Wallet
user’s account on a mobile device or another type of
TE)
MSW Multi Stop watch, tool for time-taking of events
TA Transaction
ObsTool Observer Tool: User Equipment running software for active
and passive network testing in the background
It is important to note that Digital Financial Services as applications having an internal functionality which
in most cases cannot be understood as "standard- is not known to the general public and may also
ized services" like telephony or facsimile, but rather change over time without prior notice.
8 TEST SCENARIO UNDER CONSIDERATION
The basic scenario under consideration is the “Person- P2P transfer; technically, received money will in this
to-Person" (P2P) money transfer in the cases: case appear to come from that particular entity rath-
er than from the actual sending entity. If reception
• Money transfer between two parties in the notifications are used for data evaluation (which is
same country, but using different DFS providers not the case in the current methodology), this would
(inter-operator scenario). have to be considered in data processing.
• Money transfer between two parties in differ- The P2P basic scenario and its modelling is described
ent countries, using the same DFS providers in detail in ITU-T Recommendation G.1033 and ITU-T
(e.g., national branches of a multi-national net- Recommendation P.1502. For the sake of convenience
work operator). of reading, the essential parts are explained here
• Money transfer between two parties in different while for more detail, the reader is kindly referred to
countries, using different DFS providers. above mentioned Recommendations.
It is important to state that the methodology for 8�1 Roles, entities and action/event flow
these variants is the same as in all these cases money In the P2P money transfer scenario, money is trans-
is transferred between two entities. There may be ferred from party A (the active party which is send-
differences in the details of an operating sequence; ing money) to party B (the receiving party.
these are, however, not greater than differences In a practical implementation if testing, each party
between same-operator, same-country operating is represented by one testing team. By practical
sequences. considerations, money is transferred in a cyclic fash-
NOTE – In some countries, the DFS service might be ion, so teams switch roles after each transfer, as
registered under the central bank, and money trans- shown in Figure 1.
fers considered to be bank transfers. This may have NOTE – The graph below only shows the basic
an effect on the appearance of respective transac- case� In order to take care of the whole spectrum
tions where, in actual implementations, it has shown of possible cases during testing, some additional,
that in some cases entities other than the sending derived cases need to be considered, which will be
party (e.g., agents) are used for cross-border trans- done in a subsequent section�
actions. From an end to end perspective, this is still a
Methodology for inter-operator and cross-border P2P money transfers 11