Page 16 - Implementation of Secure Authentication Technologies for Digital Financial Services
P. 16
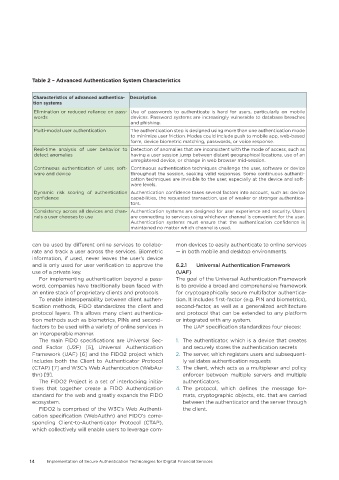
Table 2 – Advanced Authentication System Characteristics
Characteristics of advanced authentica- Description
tion systems
Elimination or reduced reliance on pass- Use of passwords to authenticate is hard for users, particularly on mobile
words devices. Password systems are increasingly vulnerable to database breaches
and phishing.
Multi-modal user authentication The authentication step is designed using more than one authentication mode
to minimize user friction. Modes could include push to mobile app, web-based
form, device biometric matching, passwords, or voice response.
Real-time analysis of user behavior to Detection of anomalies that are inconsistent with the mode of access, such as
detect anomalies having a user session jump between distant geographical locations, use of an
unregistered device, or change in web browser mid-session.
Continuous authentication of user, soft- Continuous authentication techniques challenge the user, software or device
ware and device throughout the session, seeking valid responses. Some continuous authenti-
cation techniques are invisible to the user, especially at the device and soft-
ware levels.
Dynamic risk scoring of authentication Authentication confidence takes several factors into account, such as: device
confidence capabilities, the requested transaction, use of weaker or stronger authentica-
tors.
Consistency across all devices and chan- Authentication systems are designed for user experience and security. Users
nels a user chooses to use are connecting to services using whichever channel is convenient for the user.
Authentication systems must ensure that the authentication confidence is
maintained no matter which channel is used.
can be used by different online services to collabo- mon devices to easily authenticate to online services
rate and track a user across the services. Biometric — in both mobile and desktop environments.
information, if used, never leaves the user’s device
and is only used for user verification to approve the 6.2.1 Universal Authentication Framework
use of a private key. (UAF)
For implementing authentication beyond a pass- The goal of the Universal Authentication Framework
word, companies have traditionally been faced with is to provide a broad and comprehensive framework
an entire stack of proprietary clients and protocols. for cryptographically secure multifactor authentica-
To enable interoperability between client authen- tion. It includes first-factor (e.g. PIN and biometrics),
tication methods, FIDO standardizes the client and second-factor, as well as a generalized architecture
protocol layers. This allows many client authentica- and protocol that can be extended to any platform
tion methods such as biometrics, PINs and second– or integrated with any system.
factors to be used with a variety of online services in The UAF specification standardizes four pieces:
an interoperable manner.
The main FIDO specifications are Universal Sec- 1. The authenticator, which is a device that creates
ond Factor (U2F) [5], Universal Authentication and securely stores the authentication secrets
Framework (UAF) [6] and the FIDO2 project which 2. The server, which registers users and subsequent-
includes both the Client to Authenticator Protocol ly validates authentication requests
(CTAP) [7] and W3C’s Web Authentication (WebAu- 3. The client, which acts as a multiplexer and policy
thn) [9]. enforcer between multiple servers and multiple
The FIDO2 Project is a set of interlocking initia- authenticators.
tives that together create a FIDO Authentication 4. The protocol, which defines the message for-
standard for the web and greatly expands the FIDO mats, cryptographic objects, etc. that are carried
ecosystem. between the authenticator and the server through
FIDO2 is comprised of the W3C’s Web Authenti- the client.
cation specification (WebAuthn) and FIDO’s corre-
sponding Client-to-Authenticator Protocol (CTAP),
which collectively will enable users to leverage com-
14 Implementation of Secure Authentication Technologies for Digital Financial Services