Page 30 - Digital Financial Services security assurance framework
P. 30
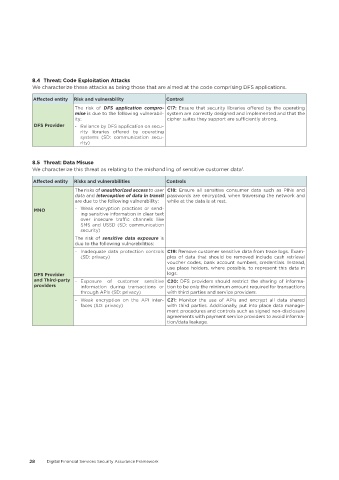
8�4 Threat: Code Exploitation Attacks
We characterize these attacks as being those that are aimed at the code comprising DFS applications.
Affected entity Risk and vulnerability Control
The risk of DFS application compro- C17: Ensure that security libraries offered by the operating
mise is due to the following vulnerabil- system are correctly designed and implemented and that the
ity: cipher suites they support are sufficiently strong.
DFS Provider - Reliance by DFS application on secu-
rity libraries offered by operating
systems (SD: communication secu-
rity)
8�5 Threat: Data Misuse
We characterize this threat as relating to the mishandling of sensitive customer data .
4
Affected entity Risks and vulnerabilities Controls
The risks of unauthorized access to user C18: Ensure all sensitive consumer data such as PINs and
data and interception of data in transit passwords are encrypted, when traversing the network and
are due to the following vulnerability: while at the data is at rest.
MNO - Weak encryption practices or send-
ing sensitive information in clear text
over insecure traffic channels like
SMS and USSD (SD: communication
security)
The risk of sensitive data exposure is
due to the following vulnerabilities:
- Inadequate data protection controls C19: Remove customer sensitive data from trace logs. Exam-
(SD: privacy) ples of data that should be removed include cash retrieval
voucher codes, bank account numbers, credentials. Instead,
use place holders, where possible, to represent this data in
DFS Provider logs.
and Third-party - Exposure of customer sensitive C20: DFS providers should restrict the sharing of informa-
providers information during transactions or tion to be only the minimum amount required for transactions
through APIs (SD: privacy) with third parties and service providers.
- Weak encryption on the API inter- C21: Monitor the use of APIs and encrypt all data shared
faces (SD: privacy) with third parties. Additionally, put into place data manage-
ment procedures and controls such as signed non-disclosure
agreements with payment service providers to avoid informa-
tion/data leakage.
28 Digital Financial Services Security Assurance Framework