Page 16 - Digital Financial Services security assurance framework
P. 16
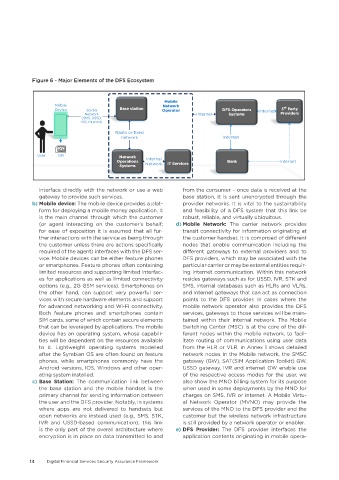
Figure 6 - Major Elements of the DFS Ecosystem
Mobile
Mobile Network rd
Device 2G/3G Base station Operator DFS Operators Internet 3 Party
Network Internet Systems Providers
(SMS, USSD,
IVR, Internet)
Radio or fixed
network Internet
User SIM Network
Operations Internal IT Services Bank Internet
Systems Network
interface directly with the network or use a web from the consumer – once data is received at the
gateway to provide such services. base station, it is sent unencrypted through the
b) Mobile device: The mobile device provides a plat- provider networks. It is vital to the sustainability
form for deploying a mobile money application. It and feasibility of a DFS system that this link be
is the main channel through which the customer robust, reliable, and virtually ubiquitous.
(or agent interacting on the customer’s behalf; d) Mobile Network: The carrier network provides
for ease of exposition it is assumed that all fur- transit connectivity for information originating at
ther interactions with the service as being through the customer handset. It is comprised of different
the customer unless there are actions specifically nodes that enable communication including the
required of the agent) interfaces with the DFS ser- different gateways to external providers and to
vice. Mobile devices can be either feature phones DFS providers, which may be associated with the
or smartphones. Feature phones often containing particular carrier or may be external entities requir-
limited resources and supporting limited interfac- ing Internet communication. Within this network
es for applications as well as limited connectivity resides gateways such as for USSD, IVR, STK and
options (e.g., 2G GSM services). Smartphones on SMS, internal databases such as HLRs and VLRs,
the other hand, can support very powerful ser- and Internet gateways that can act as connection
vices with secure hardware elements and support points to the DFS provider. In cases where the
for advanced networking and Wi-Fi connectivity. mobile network operator also provides the DFS
Both feature phones and smartphones contain services, gateways to those services will be main-
SIM cards, some of which contain secure elements tained within their internal network. The Mobile
that can be leveraged by applications. The mobile Switching Center (MSC) is at the core of the dif-
device has an operating system, whose capabili- ferent nodes within the mobile network, to facil-
ties will be dependent on the resources available itate routing of communications using user data
to it. Lightweight operating systems modelled from the HLR or VLR. in Annex 1 shows detailed
after the Symbian OS are often found on feature network nodes in the Mobile network, the SMSC
phones, while smartphones commonly have the gateway (GW), SAT(SIM Application Toolkit) GW,
Android versions, IOS, Windows and other oper- USSD gateway, IVR and internet GW enable use
ating system installed. of the respective access modes for the user, we
c) Base Station: The communication link between also show the MNO billing system for its purpose
the base station and the mobile handset is the when used in some deployments by the MNO for
primary channel for sending information between charges on SMS, IVR or internet. A Mobile Virtu-
the user and the DFS provider. Notably, in systems al Network Operator (MVNO) may provide the
where apps are not delivered to handsets but services of the MNO to the DFS provider and the
open networks are instead used (e.g., SMS, STK, customer but the wireless network infrastructure
IVR and USSD-based communication), this link is still provided by a network operator or enabler.
is the only part of the overall architecture where e) DFS Provider: The DFS provider interfaces the
encryption is in place on data transmitted to and application contents originating in mobile opera-
14 Digital Financial Services Security Assurance Framework