Page 15 - Digital Financial Services security assurance framework
P. 15
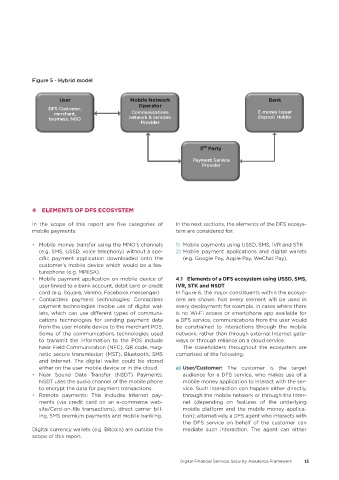
Figure 5 - Hybrid model
User Mobile Network Bank
Operator
DFS Customer,
merchant, Communications E-money Issuer
business, NGO network & services Deposit Holder
Provider
rd
3 Party
Payment Service
Provider
4 ELEMENTS OF DFS ECOSYSTEM
In the scope of this report are five categories of In the next sections, the elements of the DFS ecosys-
mobile payments: tem are considered for:
• Mobile money transfer using the MNO’s channels 1) Mobile payments using USSD, SMS, IVR and STK
(e.g. SMS, USSD, voice telephony) without a spe- 2) Mobile payment applications and digital wallets
cific payment application downloaded onto the (e.g. Google Pay, Apple Pay, WeChat Pay).
customer’s mobile device which would be a fea-
turephone (e.g. MPESA).
• Mobile payment application on mobile device of 4�1 Elements of a DFS ecosystem using USSD, SMS,
user linked to a bank account, debit card or credit IVR, STK and NSDT
card (e.g. Square, Venmo, Facebook messenger) In figure 6, the major constituents within the ecosys-
• Contactless payment technologies: Contactless tem are shown. Not every element will be used in
payment technologies involve use of digital wal- every deployment; for example, in cases where there
lets, which can use different types of communi- is no Wi-Fi access or smartphone app available for
cations technologies for sending payment data a DFS service, communications from the user would
from the user mobile device to the merchant POS. be constrained to interactions through the mobile
Some of the communications technologies used network, rather than through external Internet gate-
to transmit the information to the POS include ways or through reliance on a cloud service.
Near Field Communication (NFC), QR code, mag- The stakeholders throughout the ecosystem are
netic secure transmission (MST), Bluetooth, SMS comprised of the following:
and Internet. The digital wallet could be stored
either on the user mobile device or in the cloud. a) User/Customer: The customer is the target
• Near Sound Data Transfer (NSDT) Payments: audience for a DFS service, who makes use of a
NSDT uses the audio channel of the mobile phone mobile money application to interact with the ser-
to encrypt the data for payment transactions. vice. Such interaction can happen either directly,
• Remote payments: This includes Internet pay- through the mobile network or through the Inter-
ments (via credit card on an e-commerce web- net (depending on features of the underlying
site/Card-on-file transactions), direct carrier bill- mobile platform and the mobile money applica-
ing, SMS premium payments and mobile banking. tion); alternatively, a DFS agent who interacts with
the DFS service on behalf of the customer can
Digital currency wallets (e.g. Bitcoin) are outside the mediate such interaction. The agent can either
scope of this report.
Digital Financial Services Security Assurance Framework 13