Page 1102 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 1102
8 Assisting developing countries
6.2 Deployment models
According to [ITU-T Y.3500], the cloud economy consists of various cloud service deployment models and
service categorises. The cloud computing deployment models are described in the Table 6-1.
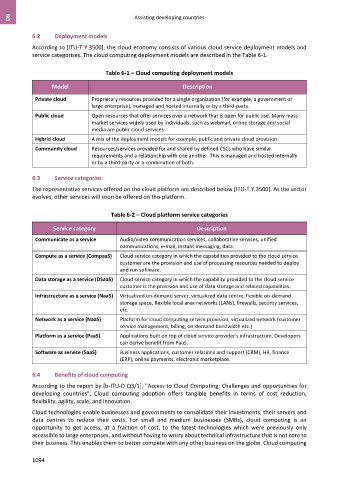
Table 6-1 – Cloud computing deployment models
Model Description
Private cloud Proprietary resources provided for a single organization (for example, a government or
large enterprise), managed and hosted internally or by a third-party.
Public cloud Open resources that offer services over a network that is open for public use. Many mass
market services widely used by individuals, such as webmail, online storage and social
media are public cloud services.
Hybrid cloud A mix of the deployment models for example, public and private cloud provision.
Community cloud Resources/services provided for and shared by defined CSCs who have similar
requirements and a relationship with one another. This is managed and hosted internally
or by a third-party or a combination of both.
6.3 Service categories
The representative services offered on the cloud platform are described below [ITU-T Y.3500]. As the sector
evolves, other services will soon be offered on this platform.
Table 6-2 – Cloud platform service categories
Service category Description
Communicate as a service Audio/video communication services, collaborative services, unified
communications, e-mail, instant messaging, data.
Compute as a service (CompaaS) Cloud service category in which the capabilities provided to the cloud service
customer are the provision and use of processing resources needed to deploy
and run software.
Data storage as a service (DSaaS) Cloud service category in which the capability provided to the cloud service
customer is the provision and use of data storage and related capabilities.
Infrastructure as a service (NaaS) Virtualized on-demand server, virtualized data centre, flexible on-demand
storage space, flexible local area networks (LANs), firewalls, security services,
etc.
Network as a service (NaaS) Platform for cloud computing service provision, virtualized network (customer
service management, billing, on-demand bandwidth etc.)
Platform as a service (PaaS) Applications built on top of cloud service provider's infrastructure. Developers
can derive benefit from PaaS.
Software as service (SaaS) Business applications, customer relations and support (CRM), HR, finance
(ERP), online payments, electronic marketplace.
6.4 Benefits of cloud computing
According to the report by [b-ITU-D Q3/1], "Access to Cloud Computing: Challenges and opportunities for
developing countries", Cloud computing adoption offers tangible benefits in terms of cost reduction,
flexibility, agility, scale, and innovation.
Cloud technologies enable businesses and governments to consolidate their investments, their servers and
data centres to reduce their costs. For small and medium businesses (SMBs), cloud computing is an
opportunity to get access, at a fraction of cost, to the latest technologies which were previously only
accessible to large enterprises, and without having to worry about technical infrastructure that is not core to
their business. This enables them to better compete with any other business on the globe. Cloud computing
1094