Page 23 - U4SSC: City Science Application Framework
P. 23
o Competence and knowledge: This factor includes the extent to which the city science
idea can be implemented by harnessing the existing knowledge and skills in the city as an
overall ecosystem.
o Regulatory and legal concerns: This factor entails various concerns and ramifications
related to regulatory and legal aspects (e.g. health, safety, privacy) within the city
regarding the city science idea.
o Ethical Issues: This factor captures various ethical concerns which may potentially arise
during and after the implementation of the city science idea.
The city can use a simple scoring system for various criteria and their sub-criteria. For example, a
simple three level (Low, Medium, High) or a five level scoring system can be adopted by the city.
The scores can be determined either quantitatively or qualitatively relying on available data and
conducted analyses, if any. Having a well-defined prioritization approach helps cities facilitate their
relative scoring among the city science ideas.
The city can apply the prioritization approach described above and can evaluate all formulated
ideas.
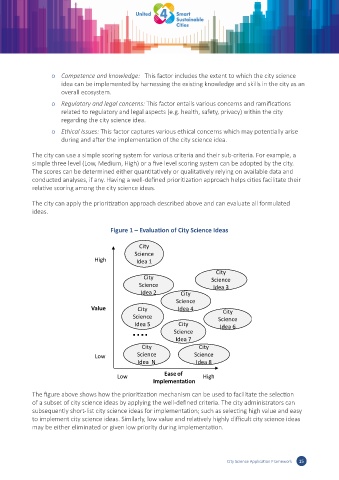
Figure 1 – Evaluation of City Science Ideas
City
Science
High Idea 1
City
City Science
Science Idea 3
Idea 2 City
Science
Value City Idea 4 City
Science Science
City
Idea 5
…. Science Idea 6
Idea 7
City City
Low Science Science
Idea N Idea 8
Low Ease of High
Implementation
The figure above shows how the prioritization mechanism can be used to facilitate the selection
of a subset of city science ideas by applying the well-defined criteria. The city administrators can
subsequently short-list city science ideas for implementation; such as selecting high value and easy
to implement city science ideas. Similarly, low value and relatively highly difficult city science ideas
may be either eliminated or given low priority during implementation.
City Science Application Framework 15