Page 17 - U4SSC: City Science Application Framework
P. 17
leases, shared basic business services and equipment, technology support services and assistance in
obtaining the financing necessary for growth .
15
On the other hand, accelerator programs can last for a certain period of time and aim to accelerate
growth for city science companies rapidly (hence the name accelerator). They aim to help develop
necessary skills for city science entrepreneurs through mentoring, formal training, informal peer
learning, and advice, among others. They target existing city science businesses and may potentially
take a holistic advisory approach to enable rapid growth.
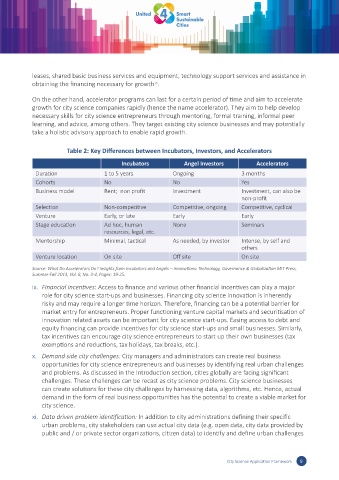
Table 2: Key Differences between Incubators, Investors, and Accelerators
Incubators Angel Investors Accelerators
Duration 1 to 5 years Ongoing 3 months
Cohorts No No Yes
Business model Rent; non profit Investment Investment, can also be
non-profit
Selection Non-competitive Competitive, ongoing Competitive, cyclical
Venture Early, or late Early Early
Stage education Ad hoc, human None Seminars
resources, legal, etc.
Mentorship Minimal, tactical As needed, by investor Intense, by self and
others
Venture location On site Off site On site
Source: What Do Accelerators Do? Insights from Incubators and Angels – Innovations: Technology, Governance & Globalization MIT Press,
Summer-Fall 2013, Vol. 8, No. 3-4, Pages: 19-25.
ix. Financial incentives: Access to finance and various other financial incentives can play a major
role for city science start-ups and businesses. Financing city science innovation is inherently
risky and may require a longer time horizon. Therefore, financing can be a potential barrier for
market entry for entrepreneurs. Proper functioning venture capital markets and securitisation of
innovation related assets can be important for city science start-ups. Easing access to debt and
equity financing can provide incentives for city science start-ups and small businesses. Similarly,
tax incentives can encourage city science entrepreneurs to start up their own businesses (tax
exemptions and reductions, tax holidays, tax breaks, etc.).
x. Demand side city challenges: City managers and administrators can create real business
opportunities for city science entrepreneurs and businesses by identifying real urban challenges
and problems. As discussed in the Introduction section, cities globally are facing significant
challenges. These challenges can be recast as city science problems. City science businesses
can create solutions for these city challenges by harnessing data, algorithms, etc. Hence, actual
demand in the form of real business opportunities has the potential to create a viable market for
city science.
xi. Data driven problem identification: In addition to city administrations defining their specific
urban problems, city stakeholders can use actual city data (e.g. open data, city data provided by
public and / or private sector organizations, citizen data) to identify and define urban challenges
City Science Application Framework 9