Page 26 - Turning digital technology innovation into climate action
P. 26
Turning digital technology innovation into climate action
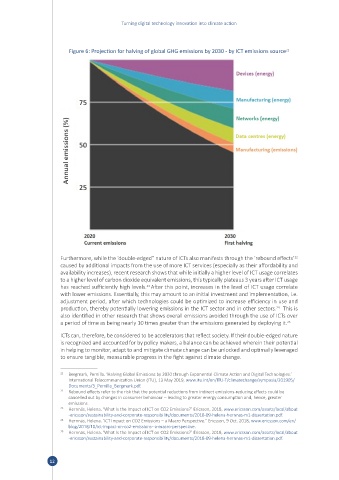
Figure 6: Projection for halving of global GHG emissions by 2030 - by ICT emissions source 21
Furthermore, while the ‘double-edged” nature of ICTs also manifests through the ‘rebound effects’
22
caused by additional impacts from the use of more ICT services (especially as their affordability and
availability increases), recent research shows that while initially a higher level of ICT usage correlates
to a higher level of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions, this typically plateaus 3 years after ICT usage
has reached sufficiently high levels. After this point, increases in the level of ICT usage correlate
23
with lower emissions. Essentially, this may amount to an initial investment and implementation, i.e.
adjustment period, after which technologies could be optimized to increase efficiency in use and
production, thereby potentially lowering emissions in the ICT sector and in other sectors. This is
24
also identified in other research that shows overall emissions avoided through the use of ICTs over
a period of time as being nearly 10 times greater than the emissions generated by deploying it.
25
ICTs can, therefore, be considered to be accelerators that reflect society. If their double-edged nature
is recognized and accounted for by policy makers, a balance can be achieved wherein their potential
in helping to monitor, adapt to and mitigate climate change can be unlocked and optimally leveraged
to ensure tangible, measurable progress in the fight against climate change.
21 Bergmark, Pernilla. ‘Halving Global Emissions by 2030 through Exponential Climate Action and Digital Technologies.’
International Telecommunication Union (ITU), 13 May 2019, www .itu .int/ en/ ITU -T/ climatechange/ symposia/ 201905/
Documents/ 3 _Pernilla _Bergmark .pdf.
22 Rebound effects refer to the risk that the potential reductions from indirect emissions-reducing effects could be
cancelled out by changes in consumer behaviour – leading to greater energy consumption and, hence, greater
emissions.
23 Hernnäs, Helena. ‘What Is the Impact of ICT on CO2 Emissions?’ Ericsson, 2018, www .ericsson .com/ assets/ local/ about
-ericsson/ sustainability -and -corporate -responsibility/ documents/ 2018 -09 -helena -hernnas -m1 -dissertation .pdf.
24 Hernnäs, Helena. ‘ICT Impact on CO2 Emissions – a Macro Perspective.” Ericsson, 9 Oct. 2018, www .ericsson .com/ en/
blog/ 2018/ 10/ ict -impact -on -co2 -emissions - -a -macro -perspective.
25 Hernnäs, Helena. ‘What Is the Impact of ICT on CO2 Emissions?’ Ericsson, 2018, www .ericsson .com/ assets/ local/ about
-ericsson/ sustainability -and -corporate -responsibility/ documents/ 2018 -09 -helena -hernnas -m1 -dissertation .pdf.
12