Page 73 - ITU Journal: Volume 2, No. 1 - Special issue - Propagation modelling for advanced future radio systems - Challenges for a congested radio spectrum
P. 73
ITU Journal: ICT Discoveries, Vol. 2(1), December 2019
= ( + ), (25) ( ̂ ⋅ ℎ ̂ ) = sin sin( − ) (34b)
( ̂ ⋅ ̂ ) = sin cos cos( − + sin cos (34c)
)
and
) (34d)
2
= + + . (26) ( ̂ ⋅ ℎ ̂ ) = −sin sin( −
2
2
2
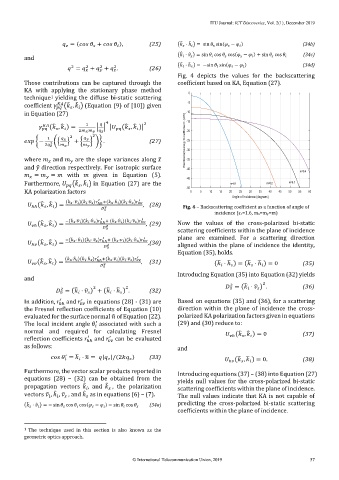
Fig. 4 depicts the values for the backscattering
Those contributions can be captured through the coefficient based on KA, Equation (27).
KA with applying the stationary phase method
technique yielding the diffuse bi-static scattering
1
̂ ̂
coefficient ( , ) (Equation (9) of [10]) given
in Equation (27)
4 2
1
̂ ̂
̂ ̂
( , ) = | | | ( , )|
2
1 2 2
{− 2 ({ } + { } )} . (27)
2
where and are the slope variances along ̂
and ̂ direction respectively. For isotropic surface
= = with given in Equation (5).
̂ ̂
Furthermore, ( , ) in Equation (27) are the
KA polarization factors
′
′
̂ ̂
ℎℎ ( , ) = ( ̂ ⋅ ̂ )( ̂ ⋅ ̂ ) ℎℎ +( ̂ ⋅ℎ ̂ )( ̂ ⋅ℎ ̂ ) , (28) Fig. 4 – Backscattering coefficient as a function of angle of
0 2
incidence (εr=1.6, mx=my=m)
′
′
̂ ̂
( , ) = −( ̂ ⋅ ̂ )( ̂ ⋅ℎ ̂ ) ℎℎ + ( ̂ ⋅ℎ ̂ )( ̂ ⋅ ̂ ) , (29) Now the values of the cross-polarized bi-static
ℎ
2
scattering coefficients within the plane of incidence
0
′ ′ plane are examined. For a scattering direction
−( ̂ ⋅ ℎ ̂ )( ̂ ⋅ ̂ )
̂ ̂
( , ) = ℎℎ + ( ̂ ⋅ )( ̂ ⋅ℎ ̂ ) , (30) aligned within the plane of incidence the identity,
ℎ
0 2
Equation (35), holds.
′
′
̂ ̂
̂
̂
̂
̂
( , ) = ( ̂ ⋅ℎ ̂ )( ̂ ⋅ℎ ̂ ) ℎℎ +( ̂ ⋅ ̂ )( ̂ ⋅ ̂ ) , (31) ( ⋅ ℎ ) = ( ⋅ ℎ ) = 0 (35)
0 2
Introducing Equation (35) into Equation (32) yields
and 2
̂
2
2
2
̂
̂
̂
0
= ( ⋅ ̂ ) + ( ⋅ ℎ ) . (32) = ( ⋅ ̂ ) . (36)
2
0
′
′
In addition, and in equations (28) - (31) are Based on equations (35) and (36), for a scattering
ℎℎ
the Fresnel reflection coefficients of Equation (10) direction within the plane of incidence the cross-
evaluated for the surface normal ̂ of Equation (22). polarized KA polarization factors given in equations
The local incident angle associated with such a (29) and (30) reduce to:
′
normal and required for calculating Fresnel ( , ) = 0 (37)
̂ ̂
′
reflection coefficients and can be evaluated ℎ
′
ℎℎ
as follows: and
= ⋅ ̂ = | |/(2 ) (33) ( , ) = 0. (38)
̂
′
̂ ̂
ℎ
Furthermore, the vector scalar products reported in Introducing equations (37) – (38) into Equation (27)
equations (28) – (32) can be obtained from the yields null values for the cross-polarized bi-static
̂
̂
propagation vectors , and , the polarization scattering coefficients within the plane of incidence.
̂
̂
vectors ̂ , ℎ , ̂ , and ℎ as in equations (6) – (7). The null values indicate that KA is not capable of
( ̂ ⋅ ̂ ) = − sin cos cos( − − sin cos (34a) predicting the cross-polarized bi-static scattering
)
coefficients within the plane of incidence.
1 The technique used in this section is also known as the
geometric optics approach.
© International Telecommunication Union, 2019 57