Page 116 - U4SSC Collection Methodology for Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
P. 116
Collection Methodology for Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
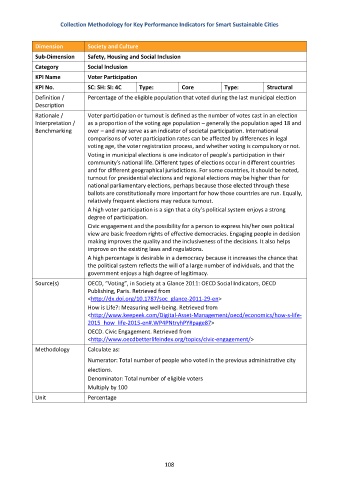
Dimension Society and Culture
Sub-Dimension Safety, Housing and Social Inclusion
Category Social Inclusion
KPI Name Voter Participation
KPI No. SC: SH: SI: 4C Type: Core Type: Structural
Definition / Percentage of the eligible population that voted during the last municipal election
Description
Rationale / Voter participation or turnout is defined as the number of votes cast in an election
Interpretation / as a proportion of the voting age population – generally the population aged 18 and
Benchmarking over – and may serve as an indicator of societal participation. International
comparisons of voter participation rates can be affected by differences in legal
voting age, the voter registration process, and whether voting is compulsory or not.
Voting in municipal elections is one indicator of people's participation in their
community's national life. Different types of elections occur in different countries
and for different geographical jurisdictions. For some countries, it should be noted,
turnout for presidential elections and regional elections may be higher than for
national parliamentary elections, perhaps because those elected through these
ballots are constitutionally more important for how those countries are run. Equally,
relatively frequent elections may reduce turnout.
A high voter participation is a sign that a city’s political system enjoys a strong
degree of participation.
Civic engagement and the possibility for a person to express his/her own political
view are basic freedom rights of effective democracies. Engaging people in decision
making improves the quality and the inclusiveness of the decisions. It also helps
improve on the existing laws and regulations.
A high percentage is desirable in a democracy because it increases the chance that
the political system reflects the will of a large number of individuals, and that the
government enjoys a high degree of legitimacy.
Source(s) OECD, “Voting”, in Society at a Glance 2011: OECD Social Indicators, OECD
Publishing, Paris. Retrieved from
<http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/soc_glance-2011-29-en>
How is Life?: Measuring well-being. Retrieved from
<http://www.keepeek.com/Digital-Asset-Management/oecd/economics/how-s-life-
2015_how_life-2015-en#.WP4PNtryhPY#page87>
OECD. Civic Engagement. Retrieved from
<http://www.oecdbetterlifeindex.org/topics/civic-engagement/>
Methodology Calculate as:
Numerator: Total number of people who voted in the previous administrative city
elections.
Denominator: Total number of eligible voters
Multiply by 100
Unit Percentage
108