Page 73 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 73
Trust in ICT 1
8.2.2 Specify trust attributes and trust relationships among entities
The trust model presented attempts to tie together all trust attributes. There is an attempt to capture the
semantics of the trust relationship using a proposed trust model and design a trust ontology that serves as
an upper level ontology for use across multiple domains. Using this trust ontology, there are the following
questions like: What are the trust relationships that an agent is participating? Is there a trust relationship
between agent X and agent Y? What is the scope of a trust relationship? What process was used to arrive at
this trust value? These questions are formulated as queries using the trust ontology in the next part.
In this part, the trust model needs cover all aspects of the trust relationship. Following the general trust
model, we can model the trust relationship between two agents as a six tuple relationship trustor, type,
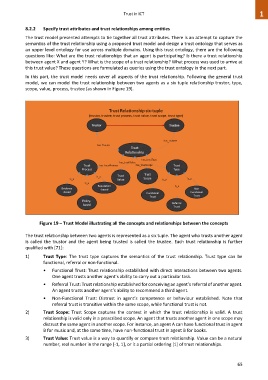
scope, value, process, trustee (as shown in Figure 19).
Figure 19 – Trust Model illustrating all the concepts and relationships between the concepts
The trust relationship between two agents is represented as a six tuple. The agent who trusts another agent
is called the trustor and the agent being trusted is called the trustee. Each trust relationship is further
qualified with [71]:
1) Trust Type: The trust type captures the semantics of the trust relationship. Trust type can be
functional, referral or non-functional.
• Functional Trust: Trust relationship established with direct interactions between two agents.
One agent trusts another agent’s ability to carry out a particular task.
• Referral Trust: Trust relationship established for conceiving an agent’s referral of another agent.
An agent trusts another agent’s ability to recommend a third agent.
• Non-Functional Trust: Distrust in agent’s competence or behaviour established. Note that
referral trust is transitive within the same scope, while functional trust is not.
2) Trust Scope: Trust Scope captures the context in which the trust relationship is valid. A trust
relationship is valid only in a prescribed scope. An agent that trusts another agent in one scope may
distrust the same agent in another scope. For instance, an agent A can have functional trust in agent
B for music and, at the same time, have non-functional trust in agent B for books.
3) Trust Value: Trust value is a way to quantify or compare trust relationship. Value can be a natural
number, real number in the range [-1, 1], or it a partial ordering [1] of trust relationships.
65