Page 70 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 70
1 Trust in ICT
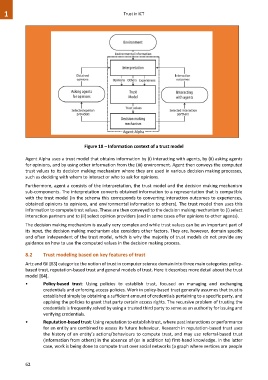
Figure 18 – Information context of a trust model
Agent Alpha uses a trust model that obtains information by (i) interacting with agents, by (ii) asking agents
for opinions, and by using other information from the (iii) environment. Agent then conveys the computed
trust values to its decision making mechanism where they are used in various decision making processes,
such as deciding with whom to interact or who to ask for opinions.
Furthermore, agent a consists of the interpretation, the trust model and the decision making mechanism
sub-components. The interpretation converts obtained information to a representation that is compatible
with the trust model (in the schema this corresponds to converting interaction outcomes to experiences,
obtained opinions to opinions, and environmental information to others). The trust model then uses this
information to compute trust values. These are then conveyed to the decision making mechanism to (i) select
interaction partners and to (ii) select opinion providers (and in some cases offer opinions to other agents).
The decision making mechanism is usually very complex and while trust values can be an important part of
its input, the decision making mechanism also considers other factors. They are, however, domain specific
and often independent of the trust model, which is why the majority of trust models do not provide any
guidance on how to use the computed values in the decision making process.
8.2 Trust modeling based on key features of trust
Artz and Gil [63] categorize the notion of trust in computer science domain into three main categories: policy-
based trust, reputation-based trust and general models of trust. Here it describes more detail about the trust
model [64].
• Policy-based trust: Using policies to establish trust, focused on managing and exchanging
credentials and enforcing access policies. Work in policy-based trust generally assumes that trust is
established simply by obtaining a sufficient amount of credentials pertaining to a specific party, and
applying the policies to grant that party certain access rights. The recursive problem of trusting the
credentials is frequently solved by using a trusted third party to serve as an authority for issuing and
verifying credentials.
• Reputation-based trust: Using reputation to establish trust, where past interactions or performance
for an entity are combined to assess its future behaviour. Research in reputation-based trust uses
the history of an entity’s actions/behaviours to compute trust, and may use referral-based trust
(information from others) in the absence of (or in addition to) first-hand knowledge. In the latter
case, work is being done to compute trust over social networks (a graph where vertices are people
62