Page 50 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 50
1 Trust in ICT
mechanisms in which reputation has been built over time based on feedbacks from both customers and
entities behaviours. These systems use several heuristics for updating reputation and integration due to the
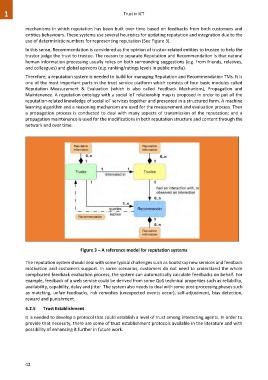
use of deterministic numbers for representing reputation (See Figure 3).
In this sense, Recommendation is considered as the opinion of trustor-related entities to trustee to help the
trustor judge the trust to trustee. The reason to separate Reputation and Recommendation is that natural
human information processing usually relies on both surrounding suggestions (e.g. from friends, relatives,
and colleagues) and global opinions (e.g. ranking/ratings levels in public media).
Therefore, a reputation system is needed to build for managing Reputation and Recommendation TMs. It is
one of the most important parts in the trust service platform which consists of four basic modules called
Reputation Measurement & Evaluation (which is also called Feedback Mechanism), Propagation and
Maintenance. A reputation ontology with a social IoT relationship map is proposed in order to put all the
reputation-related knowledge of social IoT services together and presented in a structured form. A machine
learning algorithm and a reasoning mechanism are used for the measurement and evaluation process. Then
a propagation process is conducted to deal with many aspects of transmission of the reputation; and a
propagation maintenance is used for the modifications in both reputation structure and content through the
network and over time.
Figure 3 – A reference model for reputation systems
The reputation system should deal with some typical challenges such as bootstrap new services and feedback
motivation and customers support. In some scenarios, customers do not need to understand the whole
complicated feedback evaluation process, the system can automatically calculate feedbacks on behalf. For
example, feedback of a web service could be derived from some QoS technical properties such as reliability,
availability, capability, delay and jitter. The system also needs to deal with some post-processing phases such
as matching, unfair feedbacks, risk remedies (unexpected events occur), self-adjustment, bias detection,
reward and punishment.
6.2.5 Trust Establishment
It is needed to develop a protocol that could establish a level of trust among interacting agents. In order to
provide that necessity, there are some of trust establishment protocols available in the literature and with
possibility of enhancing it further in future work.
42