Page 252 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 252
5 Trust in ICT
6.2 Trust provisioning in ICT infrastructures and services
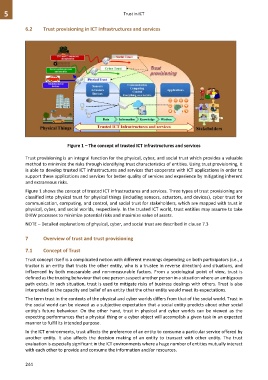
Figure 1 – The concept of trusted ICT infrastructures and services
Trust provisioning is an integral function for the physical, cyber, and social trust which provides a valuable
method to minimize the risks through identifying trust characteristics of entities. Using trust provisioning, it
is able to develop trusted ICT infrastructures and services that cooperate with ICT applications in order to
support these applications and services for better quality of services and experience by mitigating inherent
and extraneous risks.
Figure 1 shows the concept of trusted ICT infrastructures and services. Three types of trust provisioning are
classified into physical trust for physical things (including sensors, actuators, and devices), cyber trust for
communication, computing, and control, and social trust for stakeholders, which are mapped with trust in
physical, cyber, and social worlds, respectively. In the trusted ICT world, trust entities may assume to take
DIKW processes to minimize potential risks and maximize value of assets.
NOTE – Detailed explanations of physical, cyber, and social trust are described in clause 7.3
7 Overview of trust and trust provisioning
7.1 Concept of Trust
Trust concept itself is a complicated notion with different meanings depending on both participators (i.e., a
trustor is an entity that trusts the other entity, who is a trustee in reverse direction) and situations, and
influenced by both measurable and non-measurable factors. From a sociological point of view, trust is
defined as the trusting behaviour that one person suspect another person in a situation where an ambiguous
path exists. In such situation, trust is used to mitigate risks of business dealings with others. Trust is also
interpreted as the capacity and belief of an entity that the other entity would meet its expectations.
The term trust in the contexts of the physical and cyber worlds differs from that of the social world. Trust in
the social world can be viewed as a subjective expectation that a social entity predicts about other social
entity’s future behaviour. On the other hand, trust in physical and cyber worlds can be viewed as the
expecting performances that a physical thing or a cyber object will accomplish a given task in an expected
manner to fulfil its intended purpose.
In the ICT environments, trust affects the preference of an entity to consume a particular service offered by
another entity. It also affects the decision making of an entity to transact with other entity. The trust
evaluation is especially significant in the ICT environments where a huge number of entities mutually interact
with each other to provide and consume the information and/or resources.
244