Page 195 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 195
Trust in ICT 3
Service Trust Agent Trust Analysis and Service
Domain#1 Management Platform(TAMP) Other Domain #2
Trust
TA TAMPs Domain
Interface Data Trust Modelling & Evaluation Specific Data
Collecting
Social Social/Cyber/Physical
Data Trust Models
Trust Data Filtering .
Humans and Preprocessing Trust Reasoning and Evaluation . .
Context
Data Trust Metric Extractor
Trust
Cyber Service Service
Data Trust Repository & Gathering Broker Other Domain #N
S/W, Trust Knowledge
Process Domain Gathering Interfaces TAMPs Domain
Knowledge Trust Service Specific Data
Enabler Trust Data Repository
Physical Trust Trust
Data Linking IdM Trust Computation
H/W,
Devices Data Analytics Trust
Trust-based Trust Governance
Recommendation Cloud Computing API Open data,
Knowledge Base
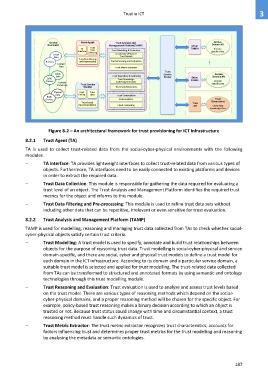
Figure 8-2 – An architectural framework for trust provisioning for ICT infrastructure
8.2.1 Trust Agent (TA)
TA is used to collect trust-related data from the social-cyber-physical environments with the following
modules.
TA Interface: TA provides lightweight interfaces to collect trust-related data from various types of
objects. Furthermore, TA interfaces need to be easily connected to existing platforms and devices
in order to extract the required data.
Trust Data Collection: This module is responsible for gathering the data required for evaluating a
trust level of an object. The Trust Analysis and Management Platform identifies the required trust
metrics for the object and informs to this module.
Trust Data Filtering and Pre-processing: This module is used to refine trust data sets without
including other data that can be repetitive, irrelevant or even sensitive for trust evaluation.
8.2.2 Trust Analysis and Management Platform (TAMP)
TAMP is used for modelling, reasoning and managing trust data collected from TAs to check whether social-
cyber-physical objects satisfy certain trust criteria.
Trust Modelling: A trust model is used to specify, annotate and build trust relationships between
objects for the purpose of reasoning trust data. Trust modelling is social-cyber-physical and service
domain-specific, and there are social, cyber and physical trust models to define a trust model for
each domain in the ICT infrastructure. According to its domain and a particular service domain, a
suitable trust model is selected and applied for trust modelling. The trust-related data collected
from TAs can be transformed to structured and annotated formats by using semantic and ontology
technologies through this trust modelling module.
Trust Reasoning and Evaluation: Trust evaluation is used to analyse and assess trust levels based
on the trust model. There are various types of reasoning methods which depend on the social-
cyber-physical domains, and a proper reasoning method will be chosen for the specific object. For
example, policy-based trust reasoning makes a binary decision according to which an object is
trusted or not. Because trust status could change with time and circumstantial context, a trust
reasoning method must handle such dynamics of trust.
Trust Metric Extractor: The trust metric extractor recognizes trust characteristics, accounts for
factors influencing trust and determines proper trust metrics for the trust modelling and reasoning
by analysing the metadata or semantic ontologies.
187