Page 191 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 191
Trust in ICT 3
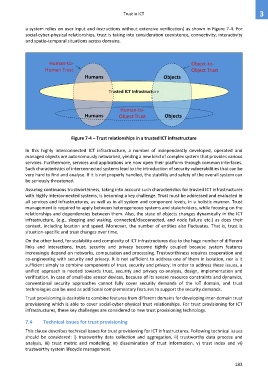
a system relies on user input and instructions without extensive verification) as shown in Figure 7-4. For
social-cyber-physical relationships, trust is taking into consideration coexistence, connectivity, interactivity
and spatio-temporal situations across domains.
Figure 7-4 – Trust relationships in a trusted ICT infrastructure
In this highly interconnected ICT infrastructure, a number of independently developed, operated and
managed objects are autonomously networked, yielding a new kind of complex system that provides various
services. Furthermore, services and applications are now open their platform through common interfaces.
Such characteristics of interconnected systems lead to the introduction of security vulnerabilities that can be
very hard to find and analyse. If it is not properly handled, the stability and safety of the overall system can
be seriously threatened.
Assuring continuous trustworthiness, taking into account such characteristics for trusted ICT infrastructures
with highly interconnected systems, is becoming a key challenge. Trust must be addressed and evaluated in
all services and infrastructures, as well as in all system and component levels, in a holistic manner. Trust
management is required to apply between heterogeneous systems and stakeholders, while focusing on the
relationships and dependencies between them. Also, the state of objects changes dynamically in the ICT
infrastructure, (e.g., sleeping and waking, connected/disconnected, and node failure etc.) as does their
context, including location and speed. Moreover, the number of entities also fluctuates. That is, trust is
situation-specific and trust changes over time.
On the other hand, for scalability and complexity of ICT infrastructures due to the huge number of different
links and interactions, trust, security and privacy become tightly coupled because system features
increasingly depend on networks, computation and processing. Trustworthiness requires cooperation and
co-engineering with security and privacy. It is not sufficient to address one of them in isolation, nor is it
sufficient simply to combine components of trust, security and privacy. In order to address these issues, a
unified approach is needed towards trust, security and privacy co-analysis, design, implementation and
verification. In case of small-size sensor devices, because of its severe resource constraints and dynamics,
conventional security approaches cannot fully cover security demands of the IoT domain, and trust
technologies can be used as additional complementary features to support the security demands.
Trust provisioning is desirable to combine features from different domains for developing inter-domain trust
provisioning which is able to cover social-cyber-physical trust relationships. For trust provisioning for ICT
infrastructures, these key challenges are considered to new trust provisioning technology.
7.4 Technical issues for trust provisioning
This clause describes technical issues for trust provisioning for ICT infrastructures. Following technical issues
should be considered: i) trustworthy data collection and aggregation, ii) trustworthy data process and
analysis, iii) trust metric and modelling, iv) dissemination of trust information, v) trust index and vi)
trustworthy system lifecycle management.
183