Page 86 - Proceedings of the 2017 ITU Kaleidoscope
P. 86
2017 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
5. PRELIMINARY CAPABILITY MATURITY Figure 3 shows the levels of maturity: Ad-hoc (less mature),
MODEL FOR SDG INDICATORS MONITORING Supported, Managed, Proficient and Optimizing (more
mature). Organizations in the Ad-hoc level are expected to
The initial/preliminary CMM explored in this research uses deliver low-quality information because their processes are
the activities (also called phases) defined by the GSBPM unclear; they rely primarily on manual practices and
[32] and classifies maturity according to a five-point scale. isolated efforts; and they have an inaccurate, partial, or
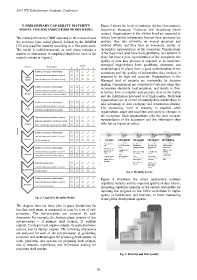
The model is multidimensional, as each phase includes a incomplete representation of the ecosystem. Organizations
number of dimensions. A simplified, high-level view of the in the Supported level have tools, platforms, and systems in
model is shown in Figure 2. place but have a poor representation of the ecosystem; the
quality of data they produce is expected to be moderate.
Managed organizations have guidelines, processes, and
methodologies in place; have a good understanding of the
ecosystem and the quality of information they produce is
expected to be high and accurate. Organizations in the
Managed level of maturity are trustworthy for decision
making. Organizations are considered Proficient when they
incorporate standards, best practices, and trends in their
activities; have a complete and accurate view of the reality
and the information produced is of high-quality. Proficient
organizations are at a level of maturity that enables them to
take advantage of data exchange and information sharing.
The Optimizing level of maturity is reached when
organizations adapt and react fast and easily to changes in
the ecosystem. Such organizations offer the most accurate
representation of the ecosystem and the information they
offer has an impact on policy.
Fig. 3: Maturity Levels
Figure 4 illustrates the direct relationship between
capability maturity and the expected quality of data. Hence,
promoting capability maturity of the entities responsible for
reporting the progress on the SDGs contributes to higher
quality of information, and therefore, to better monitoring
Fig. 2: Capability Maturity Model of the global development agenda.
The diagram does not show (due to space limitations) the
fact that each phase is composed, in turn, by a set of sub-
processes. The sub-processes are crosscut by each
dimension. For example, the Analyze phase consists of five
sub-processes – 1) prepare draft outputs, 2) validate
outputs, 3) interpret and explain outputs, 4) apply disclosure
control, and 5) finalize outputs. The following dimensions
are analyzed for each of the sub-processes: a) guidelines,
processes and methodologies for preparing draft outputs; b)
tools, platforms, and systems for preparing draft outputs;
and c) research, experience, and information sharing for
preparing draft outputs.
Fig. 4: Maturity and Data Quality
– 70 –