Page 165 - Proceedings of the 2017 ITU Kaleidoscope
P. 165
Challenges for a data-driven society
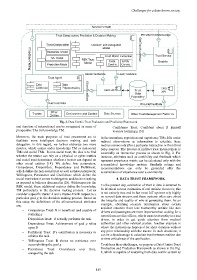
Fig. 2. Data Centric Trust Evaluation and Prediction Framework
and duration of interactions) can be recognized as some of − Confidence Trust: Confident about B himself
prospective TAs for knowledge TM. towards realizing g [31]
Moreover, the main purposes of trust assessment are to In the meantime, reputation and experience TMs falls under
facilitate more intelligent decision making and task indirect observations as information to calculate these
delegation. In this regard, we further elaborate two more metrics comes only after a particular interaction or from third
metrics, which comes under knowledge TM as non-social party sources. The process of indirect trust measurement is
TMs and social TMs. In non-social trust, the idea is to find essentially an interactive process as shown in Fig. 2. For
whether the trustor can rely on a physical or cyber entities instance, attributes such as credibility and feedback which
and social trust determines whether a trustor can depend on represent experience metric can be calculated only with the
other social entities [14]. We define four parameters; accumulated knowledge metrics. Similarly ratings and
Competence, Disposition, Dependence and Fulfilment, recommendations can only be generated after the
which define the non-social trust as well as three parameters; accumulation of experience over a community.
Willingness, Persistence and Confidence which define the
social trust when it comes to delegation and decision making 4. DATA TRUST FRAMEWORK
as opposed to believes discussed in [28]. With respect to the
REK model, these additional metrics define the knowledge To the present day, evaluation of trust in data is assumed to
TM particularly in the decision making process. Let us be identical to trust estimation of end entities. However, this
consider a specific trustor A and a trustee B with respect to a is not entirely true and in fact most IoT systems rely highly
particular goal g in the decision making process. Based on on several data streams and these systems often care about
this setup the definitions of the aforementioned attributes the integrity and quality of who is generating them. As an
are; example, obtaining accurate information about certain
− Competence Trust: B is beneficial and capable of accident situation from less trustworthy entities like taxi
drivers and passengers are more important than waiting for a
realizing g report from a police officer, who is more trustworthy to a taxi
− Disposition Trust: B actually performs the task driver, in order to get quick attention from medical
− Dependence Trust: Achievement of goal g relies authorities and other relevant parties. Another example is
upon B where the interactions happened for short duration without
− Fulfilment Trust: B’s contribution is necessary to any prior relationship with the trustee. In such situations, it
achieve the task can be a disadvantage to calculate trust between entities due
− Willingness Trust: B shows no resistance over to time criticalness of the application.
accomplishing the goal g To address these challenges, we propose a Data Centric Trust
− Persistence Trust: Consistency over time, Evaluation and Prediction Framework as shown in the Fig.
conquering the task 2, which is capable of analyzing both data centric as well as
– 149 –