Page 89 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 89
ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables 3
1) Per user’s request the NF_A needs to access the functionality provided by the NF_B. NF_A sends NF
Discovery Request including the Function Type of NF_B and/or the service related parameters, e.g.
Authentication type in case that NF_B is Authentication NF and handles one special type of
Authentication mechanism. The service related parameters help to select the special capability NF.
The Function type is used to discover the related NF instance.
2) NF Repository Function check if NF_A is authorised to access NF_B based on criteria of the NF
permission list.
3) If the request is allowed, NF Repository Function provides the candidate of NF_B’s instance to NF_A
by NF Discovery Response message based on i.e. the load level of NB’s instance. Further NF
Repository Function can store the discovery request of NF_A, and it notices the alternative instance
of NF_B to NF_A when detecting that the original instance of NB_B can’t continue to provide its
function.
4) NF_A access the NF_B instance based on the interface supported by NF_B, and the generic
communication protocol is used to transfer the messages between NF instances.
6.1.1.2.2.3 Solution 2.3: NF communication solution
(Source: ZTE)
This section addresses key issue on Network Function interconnection. In the following description, the
Network Function refers to Network Function Instance.
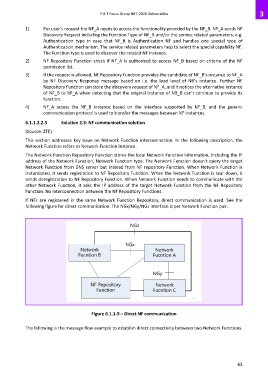
The Network Function Repository Function stores the local Network Function information, including the IP
address of the Network Function, Network Function type. The Network Function doesn’t query the target
Network Function from DNS server but instead from NF repository Function. When Network Function is
instantiated, it sends registration to NF Repository Function. When the Network Function is tear down, it
sends deregistration to NF Repository Function. When Network Function needs to communicate with the
other Network Function, it asks the IP address of the target Network Function from the NF Repository
Function. No interconnection between the NF Repository Functions.
If NFs are registered in the same Network Function Repository, direct communication is used. See the
following figure for direct communication. The NGx/NGy/NGz interface is per Network Function pair.
Figure 6.1.1-9 – Direct NF communication
The following is the message flow example to establish direct connectivity between two Network Functions.
83